Research Report: the impact of AI on search visibility and SEO in 2026
![]()
![]()
This comprehensive report examines the impact of AI on search visibility and SEO in 2026 through extensive research and analysis.
Key Research Takeaways
- Comprehensive Analysis: This report covers all major aspects of the impact of AI on search visibility and SEO in 2026
1. Executive Summary
The digital landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven largely by the rapid advancements and integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into search engines and content creation. By 2026, the impact of AI on search visibility and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategies is expected to be pervasive and fundamental, reshaping how users interact with information and how businesses vie for online attention. This executive summary provides a high-level overview of the critical findings from our research, highlighting the seismic shifts precipitated by AI, including the surge in zero-click searches, the proliferation of AI-generated content, and the subsequent evolution of SEO methodologies. The data presented here indicates a future where traditional SEO metrics are re-evaluated, content quality and authority are paramount, and adaptability to AI-driven search behaviors becomes a cornerstone of digital marketing success.
The Ascendance of Zero-Click Searches and AI-Powered Answers
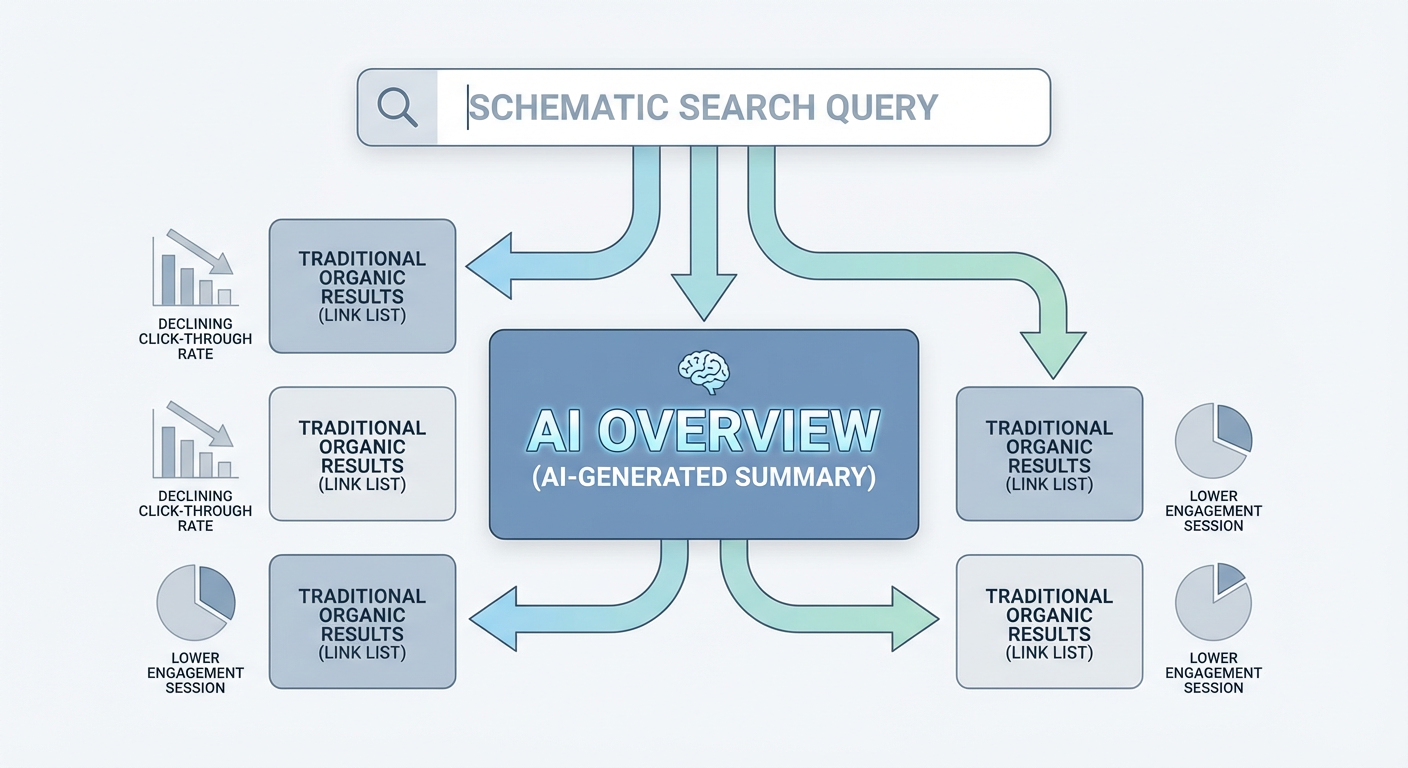
One of the most consequential trends reshaping search visibility is the dramatic increase in zero-click searches – queries that are resolved directly on the search engine results page (SERP) without the user needing to navigate to an external website. This phenomenon, which was already on an upward trajectory, has been significantly accelerated by the widespread adoption of AI-powered answer summaries and generative AI features within search engines. As of 2024, nearly 60% of Google searches in the U.S. now conclude without a click to an external site[3], a notable increase from approximately 50% in 2018[1]. The European Union mirrors this trend, with 59.7% of searches ending without a click[17]. This shift fundamentally alters the value proposition of traditional organic search rankings, as even a top position may not translate into website traffic if the query is satisfied directly on the SERP.
Google’s integration of AI-generated summaries, often termed “AI Overviews” or “Search Generative Experience” (SGE), is a primary catalyst for this surge. When an AI summary appears, the click-through rate (CTR) to traditional organic results is approximately halved, dropping from an average of 15% to 8%[4]. Furthermore, a substantial 26% of searches featuring an AI overview result in no further action from the user, compared to 16% for standard SERPs[5]. This data underscores a critical challenge for websites: while their content might be deemed relevant enough to be summarized by AI, the direct benefit of a user visit is significantly diminished. By early 2025, AI summaries were present in approximately 18% of U.S. Google queries[8], and Google itself reported over 1.5 billion monthly users engaging with AI search experiences[9]. The trajectory suggests that by 2026, AI overviews will become an even more ubiquitous feature, necessitating a re-evaluation of how website presence and success are defined beyond conventional organic traffic metrics.
Publishers and content creators have voiced strong concerns, asserting that these AI answers are responsible for “dramatically” declining web traffic[6], with some even pursuing legal action over lost visibility and alleged unauthorized use of their intellectual property[7]. For instance, Penske Media Corporation, owner of *Rolling Stone*, filed a high-profile lawsuit against Google in July 2025, accusing the tech giant of unlawfully scraping and summarizing their journalism, thereby siphoning traffic[60]. Major news outlets reported double-digit percentage drops in referral traffic, leading some to term the situation a “traffic apocalypse”[59]. Google, while acknowledging the adoption of AI features, maintains that these create “new opportunities” and disputes claims of a significant overall drop in web traffic[10]. The company highlights that it still sends billions of clicks to websites daily[34]. This tension between platforms and content providers is expected to escalate through 2026, influencing policy developments and potentially spurring new monetization models for content used by AI systems.
The Hybrid Search Landscape: Google Dominance Meets AI Chatbot Proliferation
The emergence of AI chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT has introduced a new dimension to the search landscape. ChatGPT experienced unprecedented adoption, reaching 100 million users within two months of its 2023 launch[13], making it the fastest-growing consumer application in history at that time. By March 2023, the ChatGPT website garnered 1.6 billion visits monthly, even surpassing Bing in global traffic[14]. This explosive growth signals a powerful shift in user expectation for conversational, direct answers.
Despite the rapid uptake of AI tools, traditional search engines, particularly Google, maintain considerable dominance. A February 2025 U.S. survey revealed that while 71.5% of Americans have experimented with AI search tools, 79.8% still prefer Google or Bing for general queries[15]. Only 14% of users engage with AI search daily[16], indicating that for most, AI acts as a supplement rather than a complete replacement for conventional search. This dual-track behavior is particularly evident among younger demographics, with 82% of Gen Z having tried AI search compared to 45% of Baby Boomers[17].
Microsoft’s integration of GPT-4 into Bing in 2023 provided an early test case for AI-enhanced traditional search. While it generated significant initial interest, pushing Bing to over 100 million daily active users for the first time[22] and doubling U.S. monthly active users in Q2 2023[21], its impact on overall market share remained marginal. By late 2023, Bing’s global search market share improved only slightly, from approximately 3.0% pre-AI to around 3.4%[20]. Google continues to overshadow Bing, handling over 20 times more queries, with approximately 460 million U.S. daily visits compared to Bing’s peak of 13.8 million in 2023[23]. The consensus for 2026 is that AI-driven search will largely complement, rather than replace, classic search, with Google retaining its primary gatekeeper role. However, the growth rates for AI tools suggest their influence as an alternative information discovery channel will continue to expand.
This evolving user behavior also manifests in query patterns. Users are increasingly employing longer, more conversational, and specific queries, mimicking natural language interaction with AI assistants. Google Ads data from 2022–2024 shows a nearly twofold increase in searches comprising 7-8 words since ChatGPT’s debut[30]. While short queries (<4 words) still constitute the majority of Google searches[31], the trend towards “answer-seeking” questions and detailed prompts necessitates a shift in SEO strategy towards long-tail, intent-focused keywords and content that directly addresses complex queries.
The Deluge of AI-Generated Content and the New SEO Paradigm
The accessibility of generative AI has led to an explosion of online content, fundamentally altering the competitive landscape for search visibility. By late 2025, it is estimated that over half (52%) of new online articles are primarily written by AI[27]. A more granular study in April 2025 found that 74.2% of newly created webpages contained some form of AI-generated text, with 71.7% being a human-AI mix and 2.5% fully AI-written, leaving only 25.8% as purely human-authored content[25]. This unprecedented volume means that standing out in search results is becoming increasingly difficult.
In response, search algorithms are becoming more sophisticated in discerning valuable content from mass-produced, low-quality material. Google’s March 2024 “Helpful Content” update, integrated into its core ranking system, explicitly targets “unhelpful,” possibly AI-spam content, while rewarding content demonstrating first-hand expertise and trustworthiness[29]. This accentuates the importance of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals more than ever. For marketers, the implication is clear: while AI can enhance content production efficiency, human oversight, fact-checking, and the infusion of unique insights remain critical for SEO success. Indeed, 93% of marketers continue to review and edit AI-generated content before publication[28], acknowledging the need for quality control.
The SEO industry itself has rapidly embraced AI, with 86% of professionals integrating AI into their strategies[35]. AI tools are widely used for tasks such as keyword research, content outlining, technical SEO analysis, and automating routine activities, with 75% of marketers reporting reduced time on manual tasks[37]. This efficiency has translated into tangible benefits, as 65% of businesses report better SEO results with AI assistance[38], and 52% of SEO professionals note improved on-page performance[39]. However, this widespread adoption also raises the bar for competitive advantage; innovation in strategy and creativity, rather than mere output volume, will increasingly define success.
New Search Dynamics and Evolving SEO Strategies
The shifting search landscape necessitates a recalibration of SEO strategies. A new area dubbed “Generative AI Optimization” (GAIO) is emerging, focusing on ensuring content is not only ranked by search engines but also cited and featured within AI summaries[32]. This involves optimizing structured data, creating authoritative content that AI models are likely to draw from, and monitoring citations within AI outputs. The goal shifts from merely driving clicks to securing visibility and establishing brand credibility within the AI-driven answers themselves.
Measuring success is also evolving beyond traditional click metrics. Instead of solely chasing website traffic, SEO professionals are increasingly valuing metrics like “assistant mentions” or “share of voice” within AI answers, recognizing the branding and thought leadership value even in zero-click scenarios. Content strategy is therefore prioritizing informational content less prone to AI cannibalization, such as original research, thought leadership pieces, experiential content, and in-depth guides, where a full website visit offers more value than a summarized answer. Conversely, generic FAQs or basic definitional content are becoming less effective as AI can instantly resolve such queries.
Technical SEO is also adapting. The prevalence of voice search and conversational AI elevates the importance of schema markup (e.g., FAQ, HowTo, Q&A schema), which helps search engines and AI assistants understand content context and extract precise answers. Furthermore, the debate around AI crawler management is gaining prominence, with some publishers blocking AI crawlers via robots.txt to prevent unauthorized content usage. By 2026, industry standards or legal frameworks around AI content consumption and attribution are likely to become more defined, and technical SEO practices will need to incorporate directives (e.g., `noai` tags) to manage AI access to content strategically.
Varied Industry Impacts and Adaptive Responses
The impact of AI on search visibility is not uniform across all sectors:
- Informational Sites & Blogs: These sites are both beneficiaries and victims. While they often serve as primary sources for AI summaries (Wikipedia, Reddit, and YouTube were among the top sources cited in Google’s AI summaries[42]), leading to enhanced perceived authority, the direct traffic they receive can plummet. For example, Stack Overflow experienced a 14% year-over-year traffic drop in early 2023 as developers increasingly turned to AI for coding answers[41]. Adaptations include enriching content with interactive tools, unique media, and community features to provide value beyond what an AI summary can offer.
- E-Commerce & Product Search: This sector faces significant challenges, as AI answers rarely directly link to product pages. Studies show product pages received less than 0.5% of AI referral clicks[44]. E-commerce businesses are responding by investing heavily in informational content like buying guides, comparison charts, and expert reviews, which are more likely to be featured by AI. They are also exploring integrations with voice assistants and chatbots to ensure their product catalogs are discoverable in conversational shopping contexts.
- News Publishers: Faced with a “traffic apocalypse” and allegations of content scraping, news publishers are actively redefining their relationship with AI platforms. While still experiencing significant referral traffic declines, some major players like the Associated Press[46], News Corp, and Time Magazine[47] have struck licensing deals with OpenAI and other AI companies. These agreements aim to monetize their content’s use in AI training and summaries, signaling a future where licensed content feeds AI models, ensuring attribution and potential revenue. This shift implies SEO for news will involve close collaboration with business development and legal teams on content agreements.
- Local and Service Businesses: Local search remains critical, and AI overviews often draw from Google Maps and Google Business Profile data for local queries. Optimizing these profiles with accurate and rich information (photos, reviews, FAQ content) is essential. While zero-click search could increase for simple informational queries, users will likely still click through for transactional actions like directions or bookings. Local SEO will increasingly need to account for voice search and natural language queries, ensuring specific Q&A for businesses is easily accessible to AI systems.
Key Data and Trends by 2026:
The table below summarizes key data points and their implications for search visibility and SEO in 2026.
| Metric/Trend | 2024/2025 Data | Implications for 2026 and SEO Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-Click Searches | ~60% of Google searches end without a click (up from 50% in 2018)[1]. When AI summary appears, CTR to traditional results drops from 15% to 8%[4]. 26% of AI-summary searches result in no click at all[5]. | SEO must target visibility within SERP features and AI summaries (“position zero”) rather than just high organic rankings. Brand visibility and reputation from being cited will be as important as direct high-volume traffic. Publishers face declining referral traffic and may pursue legal/licensing options. |
| AI Search Adoption | 71.5% of Americans have tried AI search, but 79.8% still prefer traditional search for most queries[15]. Only 14% use AI search daily[16]. Gen Z adoption is 82% vs. 45% for Baby Boomers[17]. | AI search is complementary, not yet a full replacement. Optimizing for both traditional search and AI platforms (e.g., specific AI answer generation) is crucial. Young demographics represent future market shifts. |
| Bing’s AI Impact | Bing’s market share rose marginally to ~3.4% globally (from ~3.0%) post-GPT-4 integration[20]. Google still processes 20x more daily visits than Bing’s peak (460M vs. 13.8M)[23]. | Google remains dominant. While optimizing for Bing’s AI features can capture niche traffic, efforts should prioritize Google’s evolving AI landscape. AI’s “game-changing” potential has not yet led to revolutionary market shifts. |
| ChatGPT Growth | Reached 100M users in 2 months (Jan 2023)[13]. 1.6bn monthly visits by March 2023, surpassing Bing[14]. | Signified a fundamental shift in user expectation for conversational interfaces. Forced major search engines to accelerate AI integration. Content must adapt to new “answer-seeking” query behaviors. |
| AI-Generated Content Volume | 52% of new online articles are AI-generated (late 2025)[27]; 74.2% of new webpages contain some AI content (Apr 2025)[25]. | Content saturation will intensify competition. SEO demands higher quality, human-edited, and uniquely valuable content. Google’s Helpful Content updates will penalize low-value, mass-produced AI spam. |
| AI in SEO Workflows | 86% of SEO professionals use AI in strategy[35]. 75% report time savings on routine tasks[37]. 65% see better SEO results with AI[38], 52% improved on-page performance[39]. | AI is an essential efficiency tool. Competitive advantage will come from strategic application and human refinement, not just raw output. Quality control (93% of marketers edit AI content[28]) is critical. |
| Query Length & Specificity | 7+ word queries nearly doubled post-ChatGPT (2022-2024)[30]. Still, only ~10% of Google searches are >7 words[31]. | SEO should increasingly target natural language, question-based queries, and long-tail keywords. Provide concise, direct answers and leverage schema markup. |
| AI Referral Traffic | 0.15% of global web traffic (mid-2025)[40], but growing 7x YoY[40]. AI visitors spend 68% more time on site than organic search visitors[40]. | Low volume now, but high growth and engagement suggest AI referrals could be a significant channel by 2026 for highly relevant content. Focus on user engagement post-click. |
| AI Traffic by Content Type | 77.3% of AI clicks go to blog/article pages[43]. <0.5% to product/e-commerce pages[44]. | Informational content (finance, tech, how-to) is favored. E-commerce sites need to build out content marketing (guides, reviews) to capture AI visibility and drive downstream conversions. |
| Publisher Responses | Traffic declines linked to AI. Some publishers suing Google[60]; others licensing content to OpenAI/Google[46][47]. Diversifying revenue (subscriptions, apps)[45]. | New revenue models emerge from licensing and direct audience relationships. SEOs in media must work with legal teams on content rights and potentially use AI crawler directives. |
In conclusion, the impact of AI on search visibility and SEO by 2026 will be characterized by a complex interplay of challenges and opportunities. While zero-click searches continue to erode traditional organic traffic, they simultaneously create new avenues for brand visibility within AI-driven summaries. The flood of AI-generated content intensifies the need for high-quality, authoritative, and human-centric content that stands out and meets Google’s evolving “Helpful Content” guidelines. SEO professionals must adopt an adaptive and sophisticated approach, leveraging AI tools for efficiency while prioritizing human creativity, ethical content practices, and a nuanced understanding of new search dynamics. The future of SEO is not just about ranking for keywords, but about optimizing for comprehensive visibility within an increasingly intelligent and conversational search ecosystem.
This executive summary sets the stage for a deeper dive into each of these areas, exploring the strategic adjustments necessary for sustained online visibility and success in the AI-driven future.
2. The Rise of Zero-Click Searches and AI Overviews
The digital landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the increasing integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into search engines and daily information retrieval. Perhaps the most significant manifestation of this shift is the dramatic rise of “zero-click searches” and the ubiquitous deployment of AI Overviews (previously known as Search Generative Experience, or SGE) prominently displayed within search engine results pages (SERPs). This section provides a deep dive into these phenomena, examining their statistical prevalence, the resulting impact on website traffic and publishers, the legal and commercial reactions from content creators, and Google’s evolving strategy in navigating this new AI-driven search paradigm. By 2026, the implications of zero-click searches and AI Overviews are expected to reshape SEO strategies, redefine content value, and fundamentally alter the relationship between search engines and the content ecosystem.
The Accelerating Trend of Zero-Click Searches
The concept of a “zero-click search” describes a user’s interaction with a search engine where their query is answered directly on the SERP, eliminating the need to click through to any external website. This phenomenon is not entirely new, having been influenced by features like featured snippets, knowledge panels, and local packs for years. However, the advent of generative AI has rapidly accelerated this trend, pushing zero-click rates to unprecedented levels and signaling a monumental shift in how users consume information online.
Current data reveals an alarming increase in these types of searches. As of 2024, nearly 60% of all Google searches in the U.S. now conclude without a single click to an external website[3]. This figure represents a significant leap from approximately 50% in 2018[1], illustrating a steady upward trajectory that is only expected to intensify through 2026 as generative AI permeates search further. In the European Union, the trend is strikingly similar, with 59.7% of searches being zero-click[2]. These numbers underscore a critical reality for publishers and website owners: a majority of searches now satisfy user intent directly on Google’s own platform, minimizing direct referral traffic to third-party sites. This means that even a highly ranking organic result might capture less direct traffic if an AI summary effectively answers the query.
The primary driver behind this recent surge is the widespread deployment of AI-powered answer summaries, prominently featured as “AI Overviews” or similar generative AI responses on the SERP. These summaries are designed to synthesize information from various sources and present a concise, direct answer to the user’s query, effectively keeping the user within the search engine’s ecosystem. This fundamental change transforms search engines from mere navigational tools to comprehensive answer engines, reducing the incentive for users to explore external links.
To illustrate the stark impact of AI Overviews on click-through rates (CTR), a March 2025 study by Pew Research Center provided compelling evidence. The study found that when Google’s AI-generated summary appeared on a search results page, users clicked a traditional result link only 8% of the time, roughly half the click rate observed on pages without an AI summary, which stood at 15%[1]. Furthermore, in 26% of searches where an AI answer was provided, the user took no further action at all, compared to 16% for classic search results[1]. This data confirms the profound disintermediating effect of AI-powered summaries, as users perceive the AI’s response as sufficient, reducing the necessity of engaging with external websites. For marketers and SEO professionals, this means that achieving a #1 organic ranking, historically the holy grail of SEO, no longer guarantees the same volume of direct traffic if an AI Overview pre-empts the click.
The implications of this accelerating zero-click trend are far-reaching. Websites that historically relied heavily on organic search traffic for their business models, particularly those in informational, news, or how-to niches, are experiencing significant impacts. The immediate consequence is a notable decline in referral traffic, which directly affects advertising revenue, subscription conversions, and overall user engagement for these external sites.
Publishers’ Reactions, Legal Challenges, and Google’s Response
The dramatic increase in zero-click searches and the direct competitive nature of AI Overviews have not gone unnoticed by content publishers. Many have openly voiced their concerns, attributing “dramatically” declining web traffic to these AI features[4]. The sentiment among publishers ranges from frustration to outright alarm, with some describing the situation as a “traffic apocalypse” for online media[12].
This discontent has escalated into legal challenges. A prominent example is the lawsuit filed in July 2025 by Penske Media Corporation, owner of major media outlets like *Rolling Stone*, against Google[13]. The lawsuit alleges that Google’s AI search snippets unlawfully scrape and summarize their copyrighted journalism, thereby siphoning off traffic and advertising revenue that would otherwise go to publisher sites. This legal action underscores a growing rift between content creators who invest significant resources in generating original material and AI systems that leverage this material to provide answers directly within the search engine interface, often without direct attribution or compensation. Penske Media’s CEO publicly criticized Google as an “intentional bad actor,” accusing the tech giant of exploiting publisher content for its AI initiatives without fair compensation[13].
Publishers, especially news organizations, have found themselves in a precarious position. As traditional search referral traffic “quickly evaporates”[12], many are actively diversifying their business models to reduce their reliance on Google. Strategies include investing heavily in subscription products, building direct audience relationships through newsletters, developing proprietary apps, and organizing events[12]. The dire predictions of a “Google Zero” scenario, where Google sends negligible meaningful traffic to publisher sites, while potentially hyperbolic, encapsulates the existential threat perceived by many in the media industry[12].
Google, while acknowledging the evolution of search, has largely pushed back against claims of significant negative impact. The company insists that its AI features, including AI Overviews, create “new opportunities” for content creators and that overall web traffic has not significantly dropped due to these changes[6]. Google reported that by early 2025, AI summaries were rolled out to approximately 18% of U.S. Google queries[7], and over 1.5 billion monthly users globally were engaging with AI search experiences[8].
While defending its position, Google has also shown signs of adaptation. It disputed the Pew study’s findings as “not representative,” asserting that it still sends “billions of clicks” to websites daily[9]. Simultaneously, it has been iterating on how AI answers are presented, for instance, by citing multiple sources. A Pew study noted that 88% of AI summaries cited three or more sources, indicating an attempt to distribute visibility among publishers and provide broader context[10]. Google also continues to emphasize its “Helpful Content” updates, which, integrated into its core ranking system in March 2024, aim to prefer trustworthy, human-friendly content and penalize low-value, AI-generated spam[10].
Looking towards 2026, it is anticipated that Google will continue to expand its AI capabilities in search, while simultaneously fine-tuning its algorithms and product features to balance user satisfaction with the sustainability of the content ecosystem. This may include refining AI Overview triggers, improving attribution mechanisms, and potentially exploring models for monetizing AI snippets or offering content creators opt-out options. For SEO professionals, staying abreast of these ongoing changes will be paramount, as influencing how content is sourced and displayed within AI Overviews could become a central aspect of visibility strategies.
AI as the New Search Competitor: Usage Habits and Market Share in 2025-2026
The emergence of AI chatbots and conversational AI models has introduced a new dimension to the search landscape, creating an alternative pathway for information retrieval that directly competes with traditional search engines. While Google maintains a dominant position, user habits are evolving, and AI-powered tools are carving out their own niche.
The consumer adoption of AI search mechanisms has been explosive. OpenAI’s ChatGPT, launched in late 2022, rapidly became the fastest-growing consumer application in history, reaching 100 million monthly users within approximately two months by January 2023[5]. By March 2023, ChatGPT was attracting an astonishing 1.6 billion visits per month globally, even surpassing the traffic of Microsoft Bing[5]. This unprecedented growth signaled a monumental shift, demonstrating a clear user appetite for conversational, AI-driven information.
By early 2025, a U.S. survey indicated that 71.5% of people had used AI tools like ChatGPT or Bing Chat for search-like tasks at least occasionally[4]. This widespread experimentation, however, has not yet translated into a full exodus from traditional search engines. The same survey found that 79.8% of users still prefer Google or Bing for most general queries[4]. Only 14% use AI search daily[4]. This suggests a complementary rather than a wholesale replacement dynamic. Users tend to leverage AI assistants for specific needs such as deeper explanations, generating creative content, or debugging code, while relying on the familiarity and authority of traditional search engines for quick factual lookups and trusted results.
Age demographics play a significant role in this adoption, with Gen Z leading the charge at 82% having tried AI search, compared to 45% of Baby Boomers[4]. This generational divide underscores a long-term trend; as younger, AI-native generations mature, the influence of AI on search behavior is likely to intensify.
Despite the rapid uptake in absolute user numbers, AI chatbots still account for a relatively small fraction of overall search volume. In 2024, a study found that the top 10 AI chatbots collectively accounted for only about 2.9% of total search/web query volume[6]. While this figure highlights Google’s enduring dominance, it also masks rapid growth. Traffic from AI search tools to publishers’ sites, though currently small (0.15% of global web traffic as of mid-2025)[10], is multiplying quickly, experiencing a 7x year-over-year growth[10]. Some industries even reported 400-900% jumps in AI-driven visits within a single quarter[7]. This indicates that while AI is not yet a volume driver, its momentum is undeniable, and it could become a significant referral channel in certain sectors by 2026.
Microsoft’s integration of GPT-4 into Bing in 2023 provides a valuable case study on the limits of AI-driven market disruption. The “new Bing” initially generated considerable excitement, leading to an increase in its daily active users to over 100 million for the first time[15]. In the U.S., Bing’s monthly active user count more than doubled in Q2 2023 following the AI integration[14]. However, this surge proved to be short-lived, with Bing’s global search market share reaching only about 3.4% by late 2023, a marginal increase from its pre-AI share of 3.0%[14]. User retention became an issue, with many users trying the new Bing Chat but few making a permanent switch[16]. Google continues to overshadow Bing massively, handling over 20 times more queries, with approximately 460 million U.S. daily visits compared to Bing’s peak of 13.8 million daily visits in 2023[17]. This suggests that entrenched user habits, Google’s superior data, and its pervasive ecosystem advantages (e.g., Chrome integration, Android defaults) remain formidable barriers to entry, even for advanced AI-enhanced competitors.
For SEO professionals, this dual-track behavior implies a need to strategize for both traditional search engine optimization and “Generative Engine Optimization” (GEO). While Google will remain the primary traffic source for most, ignoring the burgeoning AI search platforms would be a strategic misstep, especially as AI-driven search is expected to complement, rather than completely replace, classic search by 2026.
The Shifting Nature of Search Queries
Another notable evolution in search dynamics, influenced by conversational AI, is the changing nature of user queries. As users become accustomed to interacting with AI in a more natural, conversational style, their search queries are becoming longer and more specific.
Google Ads data from 2022–2024 reveals a nearly twofold increase in searches comprising 7–8 words since ChatGPT’s debut[18]. Users are increasingly phrasing their searches as full questions or detailed tasks, anticipating a direct, comprehensive answer rather than a list of links. For example, queries like, “How much is car insurance for a 2022 Honda Accord?” exemplify this shift towards specific, context-rich questions. However, it’s important to note that shorter, keyword-based queries still predominate, with only about 10% of Google searches exceeding seven words so far[19].
By 2026, experts anticipate a continued and more pronounced shift towards natural language queries and “answer-seeking” questions. This has significant implications for SEO, necessitating a renewed focus on:
- Long-tail keywords: Optimizing for more specific, multi-word phrases that reflect conversational language.
- Intent-focused content: Creating content that directly addresses specific user questions and anticipates the nuanced intent behind complex queries.
- Structured data and FAQ schema: Utilizing markup to help search engines (and AI models) better understand and extract answers from content for AI Overviews and other rich results.
- Conversational content: Developing content in a question-and-answer format or providing direct answers that AI models can easily synthesize.
This evolution demands that SEO strategies move beyond simple keyword matching to a deeper understanding of user intent and the conversational context of search.
AI-Generated Content Flood: SEO’s Quality vs. Quantity Dilemma
The rise of generative AI has ushered in an era of content super-abundance, fundamentally altering the competitive landscape for SEO. The ease and speed with which AI tools can produce diverse content types have led to an unprecedented flood of online material, posing both opportunities and significant challenges for quality control and search engine visibility.
The statistics paint a clear picture of this content deluge. By late 2025, estimates suggest that over half (52%) of all new online articles each month are authored by AI[9]. An Ahrefs study in April 2025 further corroborated this, finding that an astounding 74.2% of newly created webpages contained some form of AI-generated content[8]. While only 2.5% of these pages were entirely AI-written, a significant 71.7% featured a human-AI mix[8]. This means the vast majority of fresh content entering the web is now touched by AI, a seismic shift from just a few years prior.
This mass proliferation of AI-written content has direct implications for SEO:
- Increased Competition: The ease of generating content lowers the barrier to entry, leading to a crowded digital space where numerous entities can rapidly produce content on any given topic. This intensifies competition for visibility in search results.
- Quality Concerns: While AI can generate grammatically correct and coherent text, the quality, originality, and depth of insight often vary. The sheer volume of potentially mediocre or repurposed content poses a challenge for search engines to surface truly valuable information.
- Information Saturation: Users might struggle to find authoritative, unique, and trustworthy content amidst an overwhelming quantity of similar or generic information.
In response to this, search engines, particularly Google, have reinforced their commitment to quality. Google’s explicit stance is that “AI-generated content is fine if it’s helpful,” but it actively combats “SEO-first” content farms that leverage AI for mass production of low-value content. The **Helpful Content Update**, which Google integrated into its core ranking system in March 2024, is a direct response to this influx. This update aims to demote sites with substantial amounts of “unhelpful,” likely AI-spam content and, conversely, reward content that demonstrates first-hand expertise and provides genuine value to readers[10]. Websites that over-relied on AI for content generation without human oversight have already seen declines in their search rankings, underscoring the importance of quality control.
The dilemma for SEO in the AI era is therefore not about whether to use AI for content, but how to leverage it responsibly and effectively such that the final output aligns with evolving quality standards. This pushes SEOs towards a hybrid content creation model: utilizing AI for efficiency and scale, but crucially, complementing it with rigorous human editing, fact-checking, and the infusion of original research and unique insights. The statistic that 93% of marketers still manually review and edit AI-generated content before publishing[7] highlights a widespread recognition that unverified AI output is not commercially viable or reliable.
By 2026, successful content strategies will likely be characterized by:
- Emphasis on E-E-A-T: Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) guidelines will become even more critical. Demonstrating genuine human experience and expertise, through expert author bios, case studies, or original research, will be key to standing out.
- Originality and Depth: Content that provides unique value, conducts original research, or offers fresh perspectives will be highly prized. This could involve fewer, but more deeply researched and valuable, content pieces.
- Human Oversight: AI tools will serve as powerful assistants for drafting, research, and optimization, but human editors and subject matter experts will be indispensable for ensuring accuracy, relevance, and distinctiveness.
The quality vs. quantity dilemma will effectively be resolved by prioritizing quality as the ultimate differentiator, with AI serving as a tool to enhance, not replace, human creativity and expertise.
New Search Dynamics: How AI is Changing SEO Strategies
The tectonic shifts brought about by AI in search necessitate a re-evaluation of traditional SEO strategies. As zero-click searches rise and AI Overviews become standard, SEOs must adapt their approaches to ensure continued visibility and impact. The focus is expanding beyond merely ranking for keywords to optimizing for inclusion within AI-generated answers and understanding new metrics of success.
Optimizing for AI Visibility: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
A new facet of SEO, termed “Generative Engine Optimization” (GEO), is rapidly gaining prominence. This involves optimizing content not just for traditional search engine algorithms, but specifically for AI assistants and generative models that summarize information. The goal is to ensure content is picked up and cited by AI Overviews and other AI-powered answer systems.
To achieve this, several tactics are emerging:
- Semantic SEO: A deep understanding of topics, sub-topics, and entities helps search engines and AI models comprehend content relevance comprehensively.
- Structured Data: Implementing schema markup (e.g., FAQ, HowTo, Q&A schema) becomes even more critical. This provides explicit signals to AI models about the type of content and specific answers contained within a page, making it easier for them to extract and synthesize information.
- Authoritative Content: AI summaries often draw from established, high-authority sources. Pew Research found that platforms like Wikipedia, Reddit, and YouTube were among the top sources cited in Google’s AI summaries[10]. Therefore, building domain authority and trustworthiness remains paramount.
- Clear, Direct Answers: Structuring content to provide clear, concise answers to common questions makes it easier for AI to extract and integrate into summaries.
- Monitoring AI Citations: SEOs are beginning to track when and how their content is cited in AI results. Google’s SGE (now AI Overviews) highlights sources, and Bing Chat often footnotes links, allowing for some level of attribution tracking. By 2026, specialized analytics tools may emerge to track “AI-derived impressions” as a new metric.
The strategic objective shifts from merely driving clicks to ensuring brand visibility and credibility within AI answers, even if direct traffic is reduced.
Measuring Success Beyond Clicks
The traditional SEO metric of organic clicks and traffic is becoming an incomplete measure of success in the AI era. With the rise of zero-click searches, a “citation” or “mention” within an AI Overview, even without a click-through, carries significant branding and thought leadership value.
Marketers are beginning to redefine search visibility to include metrics such as:
- AI Mentions/Citations: The number of times a brand or its content is referenced or quoted in AI-generated answers.
- Share of Voice in AI Overviews: A measure of how frequently a brand’s content appears as a source within AI summaries for relevant queries.
- Engagement with Interactive SERP Features: As SERPs become more interactive with AI Overviews, carousels, and other dynamic elements, engagement with these features (even without a direct click to a website) becomes a valuable indicator.
This evolution calls for a more nuanced approach to SEO reporting, blending traditional traffic metrics with new AI-era visibility indicators.
Content Strategy Shifts for AI Resilience
The types of content that yield the most SEO value are also undergoing a transformation. If AI can instantly answer straightforward questions, the return on investment for creating basic FAQ articles diminishes. Consequently, content marketers are pivoting towards content types that AI is less equipped to handle autonomously.
According to a HubSpot survey, the most planned content investments were in:
- How-to guides (45%): Detailed, step-by-step instructions that require more than a simple summary.
- In-depth reviews/comparisons (37%): Content that offers detailed analysis, pros and cons, and nuanced recommendations.
- Thought leadership pieces: Original research, unique opinions, and expert analysis that AI cannot easily replicate. These content types provide a deeper value proposition that encourages users to click through for comprehensive understanding, personal expertise, or proprietary insights[20].
Conversely, “thin” content that merely regurgitates definitions or common knowledge is being deprioritized. There is a growing emphasis on **freshness** and **unique data**, such as original research, proprietary case studies, or timely analysis, which can differentiate a site and even make it a source for AI models. The new mantra for content in 2026 is to be either *deeply useful or truly original*, thereby building resilience against AI summarization.
Technical SEO and AI: Optimizing for Machine Readability and Rights
Technical SEO considerations are also evolving in the AI-influenced search landscape.
- Schema Markup: Beyond improving visibility in rich snippets, schema markup becomes crucial for AI. Explicitly marking up elements like author, publication date, reviews, and especially answer-oriented data (e.g., Q&A, HowTo) helps AI models accurately parse and interpret content.
- Voice Search Optimization: The conversational nature of AI leads to an increase in voice queries. Optimizing for natural language, asking and answering common questions, and structuring content for brevity and clarity will be essential.
- AI Crawler Management: A contentious but growing area is the management of AI crawlers like OpenAI’s GPTBot. Some publishers are blocking these bots via `robots.txt` to prevent their content from being used for AI training without consent or compensation. By 2026, industry standards or legal frameworks may formalize how AI models access and credit web content, potentially including `noai` directives in metadata.
- Intent Analysis: SEO tools are integrating AI to conduct advanced intent analysis, clustering keywords by likely user intent and even predicting which queries might trigger AI Overviews. This helps strategists determine where to invest in detailed content versus optimizing for shorter, summarized answers.
Navigating these technical complexities will be a key part of SEO best practices, ensuring content is both discoverable to the right systems and adheres to the owner’s usage preferences.
Case-by-Case: Industry Impacts and Responses
The impact of zero-click searches and AI Overviews is not uniform across all industries. Different sectors face unique challenges and opportunities, leading to varied strategic responses.
Informational Sites & Blogs
Informational websites and blogs (e.g., how-to guides, Q&A forums, encyclopedias) are particularly affected. On one hand, they are frequently the source material for AI answers. Wikipedia, Reddit, and YouTube were consistently found among the top three sources cited in Google’s AI summaries[10]. This can enhance their authority and potentially drive highly engaged users who seek more depth beyond the AI summary. On the other hand, if AI provides a complete answer, direct traffic can suffer significantly.
A notable example is Stack Overflow, a popular developer Q&A forum, which experienced a 13.9% year-on-year traffic drop in March 2023, coinciding with the rise of AI tools like ChatGPT and GitHub’s CoPilot[11]. Developers increasingly turned to AI for instant code snippets and solutions, bypassing traditional forums. Stack Overflow responded by temporarily banning AI-generated answers in December 2022 to preserve quality and subsequently launched its own AI initiatives, such as OverflowAI, to integrate AI-powered summaries into its platform, aiming to retain users. For informational sites, the strategy is to offer more than just answers—interactive tools, rich media, and community features—to provide reasons for users to click through, even if basic information is summarized by AI.
E-Commerce & Product Search
E-commerce businesses face a distinct challenge. AI answers rarely direct users straight to product pages. If a user asks for “the best laptop under $1000,” an AI might provide a curated list of recommendations without sending the user to a specific online store. Studies show that product and e-commerce pages received less than 0.5% of AI referral clicks[7].
In response, e-commerce players are:
- Content Marketing: Doubling down on informational content like buying guides, comparison charts, and expert reviews, which are more likely to be sourced by AI and capture users higher up the purchase funnel.
- Voice Commerce: Optimizing product feeds and data for integration with voice assistants and chatbots (e.g., via Microsoft’s Bing Shopping or Meta’s AI) to ensure their catalogs are discoverable in conversational commerce contexts.
By 2026, e-commerce SEO will be a dual strategy: traditional product page optimization augmented by robust informational content and seamless integration with AI shopping assistants.
News Publishers
News publishers are arguably among the most impacted. While real-time breaking news is harder for AI to summarize without context, factual and evergreen news content is susceptible. Many news organizations reported steady declines in Google referral traffic, exacerbated by AI.
The legal challenges, such as Penske Media’s lawsuit against Google[13], signify a heightened tension. However, other publishers have chosen collaboration. In July 2023, the Associated Press (AP) signed a two-year licensing agreement with OpenAI, allowing AI models to train on AP news content in exchange for compensation and access to OpenAI’s technology[13]. This proactive approach paved the way for similar deals, with News Corp and Time Magazine also striking licensing agreements with OpenAI and Google in 2024–2025[14]. These partnerships suggest a future where news content is syndicated to AI platforms, potentially through newswire-like models, ensuring publishers receive credit or revenue. For news SEO, this means close collaboration with legal and business development teams on content agreements and exploring technical measures to monitor and control AI’s use of their material.
Local and Service Businesses
AI’s impact on local search is still emerging. Google’s AI Overviews often pull local business information directly from Google Maps and Google Business Profile. For queries like “Find me a 24-hour pharmacy nearby,” AI might present a direct list of options without requiring a click to a third-party website, increasing zero-click local searches.
For local businesses, key strategies include:
- Google Business Profile Optimization: Ensuring comprehensive, accurate, and enhanced business information (photos, reviews, services) is available on Google Business Profile to maximize visibility in AI summaries.
- Voice Search Optimization: Anticipating and optimizing for natural language queries and voice commands (e.g., “What’s the best Italian restaurant near me that delivers?”).
- Local FAQ Content: Incorporating common questions and answers into their website content (e.g., “Do you offer vegan options?” for a restaurant) as AI voice searches may directly provide these answers to customers.
While zero-click might provide the initial answer, local businesses often rely on clicks for actions like directions, calls, or reservations, meaning the prompt fulfillment of transactional intent remains crucial.
Conclusion
The rise of zero-click searches and AI Overviews represents a fundamental paradigm shift in search engine behavior and user interaction. By 2026, the digital ecosystem will be characterized by greater AI integration, requiring a profound restructuring of SEO strategies. Publishers and content creators face challenges in maintaining traffic, but also new opportunities through “Generative Engine Optimization” and licensing models. Google, while driving this change, is also adapting its approach to balance innovation with ecosystem sustainability. For all stakeholders, the future of search visibility hinges on understanding these evolving dynamics, prioritizing content quality, adapting measurement criteria, and embracing a more symbiotic relationship with AI.
The next section delves into the detailed specifics of AI-powered content generation and its implications for SEO, building on the foundation of how AI Overviews have already reshaped user engagement.
3. AI as a Search Competitor: Usage Habits and Market Share
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has ushered in a transformative era for internet search, fundamentally altering user behaviors, competitive landscapes, and the very definition of search visibility. What began as experimental chatbots has rapidly evolved into sophisticated AI tools capable of providing direct answers, synthesizing information, and engaging in conversational queries. By 2026, AI is no longer a nascent technology but a formidable competitor and complement to traditional search engines, prompting a re-evaluation of established SEO strategies and market dynamics. This section delves into the profound impact of AI on search usage habits, its burgeoning market share, and the resulting recalibration of the search ecosystem, examining both the challenges and opportunities presented to businesses and content creators.
The core premise of search has historically been to act as a gateway, guiding users to relevant websites where they could find answers and information. However, AI’s ability to directly fulfill information needs on the search results page itself, or within conversational interfaces, is dramatically shifting this paradigm. This change is quantified by the undeniable rise of “zero-click searches”—instances where a user’s query is resolved directly within the search engine results page (SERP) without the need to navigate to an external website. This phenomenon, largely accelerated by AI-powered summaries and direct answers, poses a significant competitive threat to websites that traditionally relied on organic search traffic for their audience and revenue.
The discussion will explore the rapid adoption rates of AI search tools, highlighting their explosive growth despite Google’s enduring dominance. We will scrutinize how search giants like Microsoft have attempted to leverage AI to gain market share, and the nuanced reasons behind Google’s continued stronghold. Furthermore, the section will detail the observable shift towards more natural, conversational search queries, a direct consequence of user interaction with AI chatbots, and its implications for how content must be designed and optimized. The burgeoning volume of AI-generated content on the web also presents a critical paradox, simultaneously lowering the bar for content creation while elevating the importance of quality, authenticity, and human experience for true search visibility.
3.1 The Rise of Zero-Click Searches and AI Answer Engines
The most immediate and palpable impact of AI on search visibility is the dramatic increase in zero-click searches. Historically, users would type a query, review the list of blue links, and click on a result that seemed most promising. AI capabilities have fundamentally changed this interaction model. Google, for instance, has been incrementally enhancing its SERP features (featured snippets, knowledge panels, local packs) to provide direct answers, and the integration of AI-powered summaries, known as AI Overviews, has supercharged this trend.
3.1.1 The Zero-Click Phenomenon: Data and Growth
The data unequivocally illustrates this shift. In 2024, a staggering 58.5% of Google searches in the U.S. terminated without a single click to an external website[12]. This figure represents a significant increase from approximately 50% in 2018[2], indicating a steady upward trajectory that is only expected to accelerate through 2026 with the broader proliferation of generative AI in search interfaces. The European Union exhibits a similar pattern, with 59.7% of searches ending without a click[13]. This means that for nearly six out of ten searches, users are finding sufficient answers directly on Google’s platform, effectively bypassing traditional websites.
The primary driver behind this escalating zero-click rate is Google’s implementation of AI-powered answer summaries, such as AI Overview. Research conducted in March 2025 revealed a stark correlation: when an AI-generated summary appeared on a search page, the click-through rate (CTR) to traditional result links plummeted to only 8%, roughly half the CTR observed on pages without an AI summary (15%)[3]. Furthermore, in 26% of searches where an AI answer was provided, the user concluded their session without any further action, compared to just 16% for classic search results[5]. This highlights a powerful user preference for convenience and immediate gratification provided by AI-synthesized responses.
3.1.2 Implications for Website Traffic and Publisher Responses
For websites and content publishers, this trend represents a significant loss of organic traffic opportunities. What was once considered a successful outcome – ranking highly for a competitive keyword – now carries reduced guarantee of an actual visit. Publishers are increasingly vocal about the adverse effects, with some describing the situation as a “traffic apocalypse.” Leading publications like Wired have openly attributed “dramatically” declining web traffic to these direct answers and AI summaries offered by Google[6].
Google, while disputing the severity of the impact, has acknowledged the transformation in search behavior. The company insists that its AI features create “new opportunities” and that overall web traffic has not “significantly dropped”[8], claiming to still send billions of clicks to websites daily[18]. However, the qualitative and quantitative evidence from publishers suggests a different reality, particularly for those heavily reliant on informational or news content.
This tension has escalated to legal action, with entities like Penske Media Corporation (owner of *Rolling Stone*) filing high-profile lawsuits against Google in July 2025. These lawsuits allege that Google’s AI search snippets illegally scrape and summarize journalistic content, effectively diverting traffic that would otherwise go to publisher sites[7]. Such litigation underscores the growing conflict over fair use of intellectual property in the age of generative AI and may precipitate regulatory scrutiny.
Despite these disputes, Google is actively integrating and refining AI in its search operations. By early 2025, AI summaries were rolled out to approximately 18% of U.S. Google queries[9], and the company reports over 1.5 billion monthly users engaging with AI search experiences[10]. Google’s adaptation includes fine-tuning algorithms, such as the Helpful Content updates, to prioritize trustworthy and human-friendly content, a move aimed at combating the proliferation of low-quality AI-generated spam and reinforcing the value of authoritative sources[11]. For SEO professionals, this means a pivotal shift in strategy: brand visibility within AI overviews, alongside strong brand authority, can become as valuable as direct website clicks.
3.2 AI as a Direct Search Competitor: Usage Habits and Market Share
While Google integrates AI into its traditional search, a new class of AI-native search tools and chatbots has emerged as direct competitors, capturing user attention and, incrementally, market share. These tools offer a fundamentally different search experience, characterized by conversational interfaces and synthetic answer generation.
3.2.1 Explosive Growth of AI Chatbots and Their Early Impact
The launch of OpenAI’s ChatGPT in late 2022 marked a pivotal moment, demonstrating the unprecedented mainstream appetite for AI-driven conversational agents. ChatGPT achieved 100 million monthly users within just two months of its launch in early 2023[14], making it the fastest-growing consumer application in history at that time. By March 2023, the platform was attracting an astonishing 1.6 billion visits per month, even momentarily surpassing Bing in global traffic volume[15]. This rapid uptake signaled a significant shift in how users sought and processed information, compelling established search engines to accelerate their own AI integration efforts.
Consumer adoption of AI tools for search tasks has continued its upward trajectory. By February 2025, a U.S. survey indicated that 71.5% of individuals had experimented with AI search tools such as ChatGPT or Bing Chat at least occasionally[16]. Adoption rates were particularly high among younger demographics, with 82% of Gen Z users having tried AI search, compared to 45% of Baby Boomers[17]. These figures demonstrate a widespread willingness to explore AI as a search alternative or complement.
Despite the explosive growth and high trial rates, AI chatbots have not yet dethroned traditional search engines. The same 2025 survey found that 79.8% of users still prefer Google or Bing for most general queries[16], with only 14% using AI search daily[16]. This suggests that while AI tools are gaining traction, they are currently used more as a supplementary resource for deeper explanations, creative tasks, or specialized queries, rather than a primary replacement for mainstream search. In 2024, AI chatbots collectively accounted for a relatively small 2.96% of the total search query volume[19], although this share is rapidly expanding. The consensus for 2026 is that AI-driven search will largely complement, rather than completely supersede, classical search, even as the growth rates for AI tools remain exceptionally high.
3.2.2 Bing’s AI Integration: A Case Study in Modest Gains
Microsoft’s aggressive integration of OpenAI’s GPT-4 into Bing in 2023 served as a critical real-world experiment into AI’s potential to disrupt search market share. This move initially garnered significant attention and a measurable boost for Bing. Following the AI integration, Bing reported reaching over 100 million daily active users for the first time[21]. In the U.S., Bing’s monthly active users more than doubled in Q2 2023, climbing to 4.4 million by year-end[22].
However, these gains proved to be modest in the grand scheme of search dominance. By late 2023, nearly a year after its GPT-4 integration, Bing’s global search market share edged up only slightly to approximately 3.4%, from its pre-AI share of around 3.0%[20]. This demonstrates that while AI features can attract curiosity and a segment of users, they have not yet fundamentally altered Google’s overwhelming lead. Google still handles more than 20 times the number of queries compared to Bing, attracting approximately 460 million daily visits in the U.S. versus Bing’s peak of 13.8 million daily visits in 2023[23].
The Bing case highlights the immense inertia of user habits and the deep entrenchment of Google’s ecosystem (e.g., Chrome as the default browser, Android integration). Many users tried the “new Bing” out of novelty but did not make a permanent switch, indicating challenges in user retention even with advanced AI capabilities[24]. For businesses, this implies that while optimizing for Bing’s AI features offers opportunities in a less competitive landscape, Google’s impending AI updates (such as Project Gemini and other advancements expected by 2026) will remain the overarching focus for broad search marketing impact.
3.3 The New Conversational Search Paradigm: Longer Queries and Natural Language
The increasing interaction with AI chatbots has fundamentally reshaped how users formulate their needs, leading to a noticeable evolution in search query patterns. Traditional keyword-based searches are gradually giving way to more natural language, conversational, and specific queries.
Users are no longer constrained by the limitations of keyword matching; they can now pose complex questions and describe their intent more fully, expecting comprehensive answers rather than merely a list of links. Google Ads data from 2022–2024, for example, illustrates a nearly twofold increase in queries containing 7 or more words since the debut of ChatGPT[25]. This includes queries phrased as specific questions, such as “How much is car insurance for a 2022 Honda Accord?”
While this shift towards longer, more descriptive queries is evident and growing, it’s worth noting that short, succinct queries (less than 4 words) still constitute the majority of Google searches[26]. Nevertheless, the trajectory indicates a continued movement towards “answer-seeking” and natural language questions. For SEO in 2026, this carries significant implications:
- Long-Tail Keyword Optimization: The emphasis shifts further towards understanding and targeting the intent behind longer, more complex queries rather than just broad keywords.
- Content Structure: Content needs to be structured to directly answer specific questions, with clear headings, subheadings, and concise summaries that can be easily parsed by AI models and conversational interfaces.
- FAQ and Conversational Content: Integrating comprehensive FAQs and adopting a conversational tone in content will become crucial to align with user expectations and increase the likelihood of content being cited by AI summaries.
- Semantic SEO: A deeper understanding of semantic relationships between keywords and topics will be necessary to ensure content comprehensively covers user intent, anticipating follow-up questions an AI or user might have.
This evolution of query patterns mandates a proactive adjustment in SEO strategies, favoring content that caters to the sophisticated and conversational nature of AI-influenced search behavior.
3.4 The AI-Generated Content Flood: Quality vs. Quantity Dilemma
The accessibility of generative AI tools has unleashed an unprecedented volume of automatically generated content onto the web, presenting both opportunities and significant challenges for SEO and content marketers.
3.4.1 Mass Proliferation of AI-Written Content
By 2025, the web is experiencing a deluge of AI-generated text. Research from April 2025 indicated that an overwhelming 74.2% of newly created webpages contained some form of AI-generated content[27]. While only 2.5% of pages were found to be entirely AI-written, a substantial 71.7% represented a human-AI hybrid, with humans editing or enhancing AI output[28]. By late 2025, it was estimated that over half (52%) of all new online articles published each month were authored by AI[29].
This surge means content production is faster and cheaper than ever. Marketers can now scale content output from blog posts to product descriptions and social media updates at previously unimaginable rates. However, this also leads to an oversaturation of similar, often generic, and potentially low-quality content, making it increasingly difficult for any single piece to stand out in search results. The web in 2026 will be characterized by intense content competition, where quantity without inherent value will likely be penalized.
3.4.2 AI in SEO Workflows: Efficiency and Competitive Landscape
Beyond content generation, AI has become deeply embedded in SEO professionals’ workflows. A striking 86% of SEO professionals had already integrated AI into their strategies by 2025[30]. AI tools are being leveraged to automate various tasks, from expediting keyword research, content outlining, and meta-tag generation to conducting technical SEO analyses and assisting in link-building outreach through personalized email drafts.
The efficiency gains are undeniable, with 75% of marketers reporting that AI significantly reduces the time spent on manual SEO tasks[31]. This efficiency contributes to improved outcomes, as 65% of businesses experienced better SEO results with AI assistance[32], and 52% of SEO professionals observed enhanced on-page performance after deploying AI tools[33]. The downside is that these efficiency benefits are universally accessible, leveling the playing field. Competitive advantage in SEO now depends less on raw output volume and more on strategic application, critical thinking, and human creativity to differentiate content and maintain quality.
3.4.3 Quality Control and E-E-A-T as Differentiators
In response to the overwhelming influx of AI-generated content, search engines, particularly Google, are placing an even greater emphasis on content quality and authenticity. Google’s reiterated stance is that AI-generated content is acceptable “if it’s helpful,” but the company actively combats “SEO-first” content farms publishing unhelpful or spammy content. The March 2024 Helpful Content Update, integrated into Google’s core ranking system, explicitly aims to demote sites with excessive generic or auto-generated text that lacks genuine utility for readers[34].
This algorithmic evolution forces SEOs to adopt a hybrid approach. While AI can draft content for scale, human oversight, editing, fact-checking, and the infusion of original insights are paramount. The finding that 93% of marketers still manually review and edit AI-generated content before publication underscores the industry’s recognition that unchecked AI output is often unreliable and risks penalization[35].
The importance of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) in Google’s quality guidelines has intensified. Demonstrating genuine human value becomes central for content to stand out. This includes:
- Featuring expert authors and reviewers with clear credentials.
- Incorporating original research, unique data, case studies, or first-hand experience.
- Building a strong brand reputation that algorithms can recognize as authoritative and trustworthy.
By 2026, successful content strategies will use AI for efficiency but prioritize human expertise for depth, uniqueness, and adherence to E-E-A-T principles. The goal is to produce content that is either deeply useful or truly original, capable of rising above the abundant AI-generated noise. The “slow content” movement—fewer but higher-quality posts—is emerging as a strategic response to the AI content flood, focusing on sustained authority over ephemeral volume.
3.5 New Avenues for Visibility: Optimizing for AI
As AI reshapes search, SEO professionals are adapting their strategies beyond traditional ranking factors to encompass optimization for AI visibility, blurring the lines between direct clicks and brand impressions.
3.5.1 Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
A new facet of SEO, termed “Generative Engine Optimization” or GEO, is gaining prominence. This involves structuring content in ways that make it highly digestible and quotable for AI models generating summaries. Key elements include:
- Clear, Well-Sourced Answers: Crafting content that provides direct, concise answers to common questions, ideal for AI to extract and synthesize.
- Structured Data Implementation: Extensive use of schema markup (FAQPage, HowTo, Q&A) helps AI better understand the context and components of content.
- Building Authority: AI summaries frequently draw from highly authoritative sources already trusted in the knowledge graph (e.g., Wikipedia, government sites, well-established news organizations)[36]. Building strong domain authority and expertise remains crucial.
Monitoring tools that indicate when specific content or brands are cited in AI summaries will become standard, shifting focus from merely traffic generation to comprehensive brand mentions within AI-powered results.
3.5.2 Redefining Success Metrics Beyond Clicks
With increasing zero-click phenomena, the definition of search success is broadening. An AI overview might provide an answer and cite a brand without generating a direct click. Such instances still hold value as brand impressions or indicators of thought leadership. Marketers are beginning to track metrics like “assistant mentions” or “share of voice in AI answers” as indicators of success. The aim is to achieve on-page visibility—being featured directly in snippets or AI cards—even if it doesn’t immediately translate into traffic. By 2026, SEO reports are expected to include both traditional metrics (rankings, organic traffic, conversions) and AI-era metrics (AI impressions, featured snippet visibility, brand citations by AI, engagement with interactive SERP features), acknowledging a more nuanced picture of search performance.
3.5.3 Content Strategy Adjustments for AI Resilience
Content strategies are undergoing a significant re-evaluation. Basic informational queries (e.g., “what is X?”) are increasingly being answered directly by AI, reducing the ROI for creating generic FAQ articles. Instead, the focus is shifting towards content that AI is less capable of fully replicating or that provides a deeper user experience:
- In-depth Guides and Thought Leadership: Content types like “how-to guides” (45% of planned investments) and “in-depth reviews/comparisons” (37% of planned investments) are being prioritized[37]. These offer value beyond a simple summary, often requiring direct user engagement.
- Original Research and Experiential Content: Content featuring unique data, original research, case studies, or personal experiences offers a differentiator that AI models cannot easily generate or synthesize.
- Engagement-focused Content: Interactive tools, rich media, and community features provide reasons for users to click through, even if basic information is provided by AI.
The strategic imperative is to create content that is either profoundly useful or genuinely unique, thereby becoming “resilient” to AI summarization and preventing traffic cannibalization.
3.5.4 Technical SEO and AI Management
Technical SEO practices are also adapting to the AI landscape:
- Schema Markup: Beyond basic schema, specific markups like Q&A and HowTo become critical for AI and conversational search platforms to understand and utilize content.
- AI Crawler Management: Publishers are actively debating and implementing strategies to manage AI crawlers (e.g., OpenAI’s GPTBot). Some are blocking these crawlers via `robots.txt` to prevent unauthorized content usage, while others are developing licensing agreements. By 2026, we may see industry standards or even legal frameworks regarding AI access and attribution, alongside emerging indexing metadata (e.g., ‘noai’ directives) for content protection.
These technical considerations ensure that content is both discoverable by relevant AI systems and protected from misuse, becoming an integral part of holistic SEO practices.
3.6 Case-by-Case: Industry Impacts and Responses
The impact of AI as a search competitor is not uniform across all industries; rather, it creates a heterogeneous landscape of winners and losers, opportunities and existential threats.
3.6.1 Informational Sites & Blogs
Informational sites, including educational blogs, Q&A forums, and encyclopedic resources, face a double-edged sword. On one hand, they frequently serve as the foundational source material for AI answers. Wikipedia, Reddit, and YouTube were among the top three sources cited in Google’s AI summaries, indicating their authority[38]. This strengthens their authority and offers brand visibility, potentially prompting users to “dig deeper” on their sites.
Conversely, if AI provides comprehensive answers, click-through rates decline. The popular developer forum Stack Overflow, for instance, experienced a 13.9% year-on-year traffic drop in March 2023, largely attributed to developers seeking coding answers directly from AI tools like ChatGPT and GitHub’s CoPilot[39]. Stack Overflow has responded by enhancing its internal AI functions and prioritizing expert-verified content to retain its audience. Informational sites must differentiate by offering more than just answers—interactive tools, rich multimedia, and community engagement—to provide compelling reasons for direct visitation.
3.6.2 E-Commerce & Product Search
E-commerce businesses encounter a specific challenge: AI answers typically don’t direct users to product pages. Studies show that product pages received less than 0.5% of AI referral clicks[40]. If a user queries for “best laptop under $1000,” an AI might generate a recommendation list without linking to specific retail sites, interrupting the sales funnels.
To counter this, e-commerce strategies are shifting toward extensive content marketing, such as buying guides, comparison charts, and in-depth reviews, which can be cited by AI and increase overall brand visibility. Furthermore, integrating product feeds with voice assistants and AI platforms (like Bing or Meta AI) is crucial for ensuring product accessibility in conversational commerce scenarios. By 2026, e-commerce SEO will heavily rely on optimizing both informational content and product data feeds for AI consumption, alongside traditional product page optimization.
3.6.3 News Publishers
News publishers face a profound existential challenge. While AI sometimes struggles with real-time news summarization, the general trend toward AI providing quick digests deeply threatens traditional news consumption models. Publishers have reported significant declines in Google referral traffic, with some, like Wired’s editor, publicly describing a “traffic apocalypse”[41].
In response, many publishers are diversifiying their revenue and audience acquisition strategies beyond reliance on Google. This includes investing in subscription models, direct-to-consumer newsletters, apps, and events[42]. Legal action, such as the *Rolling Stone* publisher’s lawsuit against Google[43], is another manifestation of this pushback.
However, a pragmatic approach is also emerging. The Associated Press, in 2023, struck a two-year licensing deal with OpenAI to provide its news archives for AI model training in exchange for compensation and access to AI tools[44]. Other major publishers, including News Corp and Time Magazine, followed suit in 2024–2025, signing similar content licensing agreements with AI developers[45]. This emerging model suggests that by 2026, many news organizations will likely license their content to AI platforms, ensuring proper attribution and revenue generation when AI synthesizes their stories. SEO professionals in news will need to collaborate closely with business and legal teams on content syndication and utilize technical measures (e.g., `crawler.txt` or content fingerprinting) to manage AI access and usage.
3.6.4 Local and Service Businesses
The impact on local search and service-based businesses is still evolving. Google’s AI Overview often leverages Google Maps and Google Business Profile data for local queries, potentially displaying direct lists of businesses. Ensuring accurate and enriched business data (photos, reviews, descriptions) is paramount so that if AI references a business, it presents compelling information.
While there is concern about increased zero-click scenarios (e.g., an AI providing a direct answer for “24-hour pharmacy nearby”), users for local services often still need to click through to transact (get directions, call, book an appointment). Local SEO in 2026 will increasingly involve optimizing for voice search and natural language queries, anticipating human-like questions. Businesses should proactively incorporate specific Q&A content (e.g., “Do you offer vegan options?” for a restaurant) as these precise answers are likely to be directly retrieved and spoken by AI voice assistants.
3.7 Notable Examples Illustrating AI’s Competitive Impact
Several real-world examples highlight the dynamic interplay between AI, search, and content visibility.
3.7.1 Bing’s GPT-4 Integration Boosts Usage (2023)
Microsoft’s integration of GPT-4 into Bing in February 2023 represented a significant attempt to challenge Google’s search hegemony. This “new Bing” initially garnered immense interest, pushing Bing to over 100 million daily active users for the first time[46], and doubling its U.S. monthly active users in Q2 2023[47]. However, this surge proved transient. By late 2023, Bing’s global search share only marginally increased to 3.4% from approximately 3% previously[48]. This case demonstrated that advanced AI features can attract initial curiosity and some niche adoption, but overcoming deeply ingrained user habits and Google’s ecosystem dominance remains a formidable challenge. For businesses, it reinforces the need to prioritize Google optimization while strategically tapping into platforms like Bing for incremental gains.
3.7.2 Stack Overflow Traffic Decline due to AI Q&A (2022–2023)
The experience of Stack Overflow offers a cautionary tale. This popular developer Q&A forum witnessed a notable 13.9% year-on-year traffic reduction in March 2023, largely correlated with the rise of AI coding assistants like ChatGPT and GitHub CoPilot[49]. Developers increasingly turned directly to AI for code snippets and problem-solving, bypassing traditional search and forum interactions. Stack Overflow’s response included temporarily banning AI-generated answers to ensure content quality and later, a strategic investment in its own AI initiatives (e.g., OverflowAI), aiming to integrate AI summaries and search directly onto its platform. This case underscores the vulnerability of platforms whose core value proposition can be replicated or disintermediated by AI, emphasizing the necessity of rapid adaptation and a focus on unique community value.
3.7.3 Rolling Stone Publisher Lawsuit Against Google (2025)
The July 2025 lawsuit filed by Penske Media Corporation (owner of *Rolling Stone*) against Google epitomizes the tensions between content creators and AI-driven search. The suit alleges that Google’s AI search snippets unlawfully scrape and summarize journalistic content, thereby siphoning traffic and revenue from publishers[50]. This action highlights the growing legal and ethical complexities surrounding AI’s use of copyrighted material. While ongoing, this lawsuit has spurred increased discussions around content licensing and could pave the way for new industry standards, such as opt-out mechanisms for AI processing or revenue-sharing models for content usage. It signals that content owners are actively seeking to protect their intellectual property rights and potentially monetize their data in the AI era.
3.7.4 Associated Press Licenses Content to OpenAI (2023)
In stark contrast to confrontation, the Associated Press (AP) took a proactive collaborative stance in July 2023, signing a two-year licensing agreement with OpenAI[51]. This deal allowed OpenAI to use a portion of AP’s news archives for training its models, providing AP with compensation and access to OpenAI’s technology. This pioneering agreement set a precedent for content creators to monetize their data when it is used by AI systems. Subsequently, other major publishers adopted similar strategies[52]. This trend suggests that by 2026, licensing agreements may become a common strategy for content producers to derive new revenue streams from AI, transforming a potential threat into a business opportunity. It reinforces the long-term value of creating high-quality, proprietary content that can be licensed as data for AI training, complementing, and even enhancing its traditional role for search visibility.
The profound changes triggered by AI in search visibility and SEO require continuous monitoring and adaptation. The lines between direct search, AI interaction, and content consumption are increasingly blurred. Understanding these shifts is crucial for developing resilient and effective digital strategies in 2026 and beyond.
This evolving landscape necessitates a deep dive into the practical actions that businesses and SEO professionals can take to navigate these changes. The next section will focus on “Actionable Strategies for SEO in the AI Era,” outlining concrete steps to optimize for both traditional and AI-influenced search environments.
4. The AI-Generated Content Deluge and Quality Dilemma
The digital landscape in 2026 is grappling with a profound transformation driven by the widespread adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in content creation and search. This era is characterized by an unprecedented deluge of AI-generated content (AIGC) flooding the web, creating both immense opportunities for efficiency and significant challenges for content quality, saturation, and visibility in search engine results. The integration of AI into SEO workflows has become almost universal, yet the critical importance of human quality control, coupled with Google’s emphasis on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), has emerged as the primary differentiator for achieving and maintaining search visibility. This section delves into the scale of AI content proliferation, its implications for competitive dynamics, how SEO professionals are adapting, and the enduring necessity of human-centric content strategies.
The Unprecedented Proliferation of AI-Generated Content
The speed and volume at which AI can produce text have reshaped the internet’s content ecosystem. What was once the domain of human writers, editors, and researchers is now increasingly augmented, or even fully replaced, by sophisticated AI models. This mass production capabilities, while democratizing content creation, has led to a significant increase in content volume, creating a highly saturated and competitive environment.
Recent studies unequivocally highlight the scale of this content deluge:
- An Ahrefs study conducted in April 2025 across 900,000 newly created webpages revealed that a staggering 74.2% contained some form of AI-generated content[8]. This suggests that only 25.8% of new pages were purely human-written[8].
- Further breaking down this figure, the Ahrefs research found that 71.7% of pages incorporated a mix of human and AI input, while a smaller but still significant 2.5% were entirely AI-written[8].
- By late 2025, a broader analysis estimated that over half (52%) of all new online articles published each month were authored by AI[9].
This dramatic shift represents a seismic change from just a few years prior, when AI-generated text was largely experimental or used for specialized, low-stakes content. The implication for publishers, businesses, and SEOs is profound: the internet is exponentially expanding its content footprint, making it increasingly difficult for individual pieces to gain visibility through sheer volume. The ability to generate articles, product descriptions, reviews, and social media posts at an unprecedented scale and low cost has lowered the barrier to entry for content creation, intensifying competition across virtually all niches.
This content explosion raises critical questions about originality, factual accuracy, and overall informational value. Search engines, particularly Google, are actively calibrating their algorithms to discern high-quality, helpful content from the rapidly expanding pool of potentially low-value, machine-generated text.
AI Integration into SEO Workflows: Efficiency vs. Competitive Saturation
The impact of AI isn’t limited to content generation; it has pervaded the entire SEO discipline. Marketing professionals and SEO teams have swiftly adopted AI tools to streamline various tasks, leading to significant efficiency gains, but simultaneously contributing to the competitive content landscape.
Key statistics illustrate AI’s widespread adoption in SEO:
- A robust 86% of SEO professionals have already integrated AI into their strategic workflows[17]. This demonstrates a near-universal embrace of AI as a fundamental tool in modern SEO.
- Marketers overwhelmingly leverage AI for automation; 67% identify generative AI as most beneficial for automating routine tasks such as drafting content outlines, generating initial content drafts, or performing data analysis[18].
- The primary driver for this adoption is time-saving: 75% of marketers report that AI has significantly reduced the time spent on manual SEO tasks, including keyword research, meta tag optimization, and content outlining[19].
- Measurable results are also a factor, with 65% of businesses reporting improved SEO outcomes through AI assistance[20]. Furthermore, 52% of SEO professionals have observed an improvement in on-page performance directly attributable to their use of AI tools[21].
These figures underscore that AI is not merely a novelty but a deeply embedded and effective component of contemporary SEO. AI tools assist with:
- **Keyword Research:** Identifying long-tail keywords, semantically related terms, and emerging topics, as well as clustering keywords by intent.
- **Content Outlining:** Generating structured outlines for articles, blog posts, and landing pages, ensuring comprehensive coverage of a topic.
- **Content Drafts:** Producing initial drafts of various content types, from blog posts to social media updates, significantly accelerating initial production.
- **Technical SEO:** Assisting with log file analysis, identifying technical issues, and even drafting code for schema markup.
- **Competitive Analysis:** Rapidly analyzing competitor content strategies, keyword targeting, and backlink profiles.
- **Link Building:** Drafting personalized outreach emails for link acquisition campaigns.
The efficiency gains are undeniable. In-house SEO teams can essentially double their productivity, allowing them to target a wider range of keywords, refresh existing content more frequently, or pursue more ambitious content marketing strategies. However, this widespread adoption also creates a new challenge: if nearly every competitor is leveraging AI for similar tasks, the playing field becomes increasingly level in terms of production capacity. The competitive advantage, therefore, must shift away from mere output volume and towards strategic application, creativity, and, critically, quality. The ease of generating content at scale means that the content market becomes even more saturated, making it harder for any mediocre piece, regardless of how quickly it was produced, to truly stand out.
The Critical Importance of Human Quality Control and E-E-A-T
Amidst the surge of AI-generated content, the imperative for human quality control and the demonstration of genuine expertise has become paramount. Google, as the dominant search engine, has consistently refined its algorithms to prioritize helpful, high-quality, and trustworthy content, a stance that has only intensified with the AI deluge.
Google’s perspective is clear: AI-generated content is acceptable “if it’s helpful”[22]. The core distinction lies in its utility and value to the user, not merely its origin. To combat the potential for low-quality, AI-spam content designed solely for search engine manipulation, Google integrated its “Helpful Content” algorithm into its core ranking system in March 2024[10]. This update specifically targets and demotes websites that publish “unhelpful” or “auto-generated content” created primarily for search engines rather than human readers[10]. Websites that aggressively leveraged AI for mass content production without sufficient human oversight often experienced significant ranking declines following these updates.
This focus on quality reinforces Google’s long-standing emphasis on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness). For content creators and SEOs, E-E-A-T serves as a crucial framework for navigating the AI content landscape:
- Experience: This refers to content creators demonstrating first-hand experience with the subject matter. For example, a product review written by someone who has genuinely used the product, or a travel guide authored by someone who has visited the location.
- Expertise: Content should be produced by individuals or organizations with demonstrable knowledge and skills in a particular field. This requires more than just academic credentials; it encompasses practical understanding and insight.
- Authoritativeness: This relates to the content creator’s or website’s reputation as a reliable source of information on a given topic. It is built through consistent high-quality output, industry recognition, and meaningful mentions from other authoritative sources.
- Trustworthiness: Fundamentally, users and search engines need to trust the information presented. This involves accuracy, transparency, secure website practices, and a clear editorial process.
The data reveals that even with powerful AI tools, human oversight remains indispensable. A 2025 survey of 879 content marketers found that while 87% use AI for content creation, a critical 93% still manually review and edit AI-generated content before publishing[22]. This high percentage underscores a widespread acknowledgment among marketers that raw AI output is not consistently reliable enough for direct publication. The reasons vary but often include:
- Accuracy: AI models can “hallucinate” or provide incorrect information, requiring rigorous fact-checking.
- Nuance and Tone: AI may lack the nuanced understanding of a brand’s voice, target audience, or the subtle context of a topic.
- Originality and Insight: While AI can synthesize existing information, it struggles to provide truly novel insights, original research, or unique perspectives rooted in personal experience.
- Helpfulness: Google’s algorithms, especially those related to Helpful Content, are designed to reward content that genuinely assists users, often requiring a human touch to anticipate and address user needs beyond what a bot can infer.
Therefore, the prevailing sentiment and strategic direction by 2026 is towards a hybrid approach:
- AI for Scale: Utilizing AI for initial content drafts, research summaries, data analysis, and automation of repetitive tasks to boost efficiency and output volume.
- Human for Depth and Quality: Employing human experts for critical editing, fact-checking, injecting original insights, validating claims, and refining content to align with E-E-A-T principles. This includes adding specific case studies, proprietary data, unique perspectives, and compelling narratives that AI cannot replicate.
SEO strategies are evolving to meet this dual requirement. Tactics include:
- Highlighting author credentials and biographical information on content pages.
- Incorporating original research, surveys, and proprietary data that AI models cannot easily replicate.
- Featuring expert quotes and interviews.
- Developing detailed “About Us” and “Contact Us” pages that clearly establish organizational trustworthiness.
- Publishing fewer, but more deeply researched and meticulously edited, articles as a response to the AI content flood, focusing on truly standing out rather than merely adding to the noise.
The quality dilemma posed by the AI content deluge means that by 2026, an effective SEO strategy will depend less on simply producing content and more on producing *exceptionally helpful, credible, and human-verified* content that resonates with both users and Google’s sophisticated ranking algorithms.
Zero-Click Searches and the Evolution of Search Visibility
The proliferation of AI directly correlates with a significant increase in “zero-click” searches, where users find their answers directly on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) without needing to click through to an external website. This phenomenon dramatically impacts traditional notions of search visibility and organic traffic.
The trend of zero-click searches has been accelerating, becoming a dominant factor in search behavior:
- As of 2024, approximately 58.5% of Google searches in the U.S. conclude without a single click to a website[1]. This figure is mirrored in the EU, standing at 59.7%[3]. This represents a notable increase from roughly 50% in 2018[2].
- The introduction of generative AI features, such as Google’s AI Overview (SGE), exacerbates this trend. A Pew Research Center study from July 2025 indicated that when an AI-generated summary appeared, the click-through rate (CTR) to traditional result links approximately halved, dropping from 15% to just 8%[1].
- Furthermore, in 26% of searches that included an AI summary, users took no further action, completing their search session on the SERP itself[1]. This is compared to 16% for classic search results without AI summaries[1].
This data confirms that AI-powered summaries fulfill user queries directly on the results page, diminishing the need to visit external sites for information. Publishers and content creators have vocally expressed concerns, with many attributing “dramatically declining web traffic” to these direct answers and AI-driven features[5]. Some media outlets describe this as a “traffic apocalypse” and are even pursuing legal action over alleged lost visibility and misuse of content[12].
Google, while acknowledging the role of AI, has insisted that these features create “new opportunities” and that overall web traffic has not significantly dropped from their perspective[6]. The company highlights that AI summaries cite “billions of clicks” to sites daily and that AI allows users to ask more questions, potentially leading to new search journeys[6]. Indeed, AI Overviews frequently cite multiple sources – 88% of AI summaries cite three or more sources[7] – presenting an opportunity for citation and brand exposure, even without a direct click.
For SEO professionals, the strategy for search visibility must evolve beyond solely chasing traditional clicks. It now includes:
- **Generative AI Optimization (GEO):** Actively working to ensure content is optimized to be cited within AI summaries. This involves clear, concise answer structures, strong E-E-A-T signals, and potentially using specific schemas or content formatting that AI models can easily parse.
- **Brand Visibility on the SERP:** Understanding that being cited or featured in an AI answer, even without a click, can serve as a powerful branding impression and establish thought leadership. The goal shifts from generating traffic to influencing the initial answer provided by the AI.
- **Measuring New Metrics:** Expanding analytics beyond traditional organic clicks to include metrics like “AI mentions,” “share of voice in AI answers,” or impressions within interactive SERP features.
- **Strategic Content Creation:** Prioritizing content types that are less prone to AI “cannibalization.” This means focusing on original research, unique perspectives, in-depth tutorials, experiential content, and complex problem-solving that AI cannot fully summarize without losing context or value.
By 2026, the success of a digital presence will be determined not just by how many clicks a website receives, but also by how effectively its content contributes to and is recognized within the AI-driven answers presented directly on the search results page.
The Shifting Role of Content Strategy: From FAQs to E-E-A-T Fortification
The impact of AI on search has fundamentally reshaped effective content strategy. What once constituted successful SEO content – readily available information, basic definitions, and common questions – is now often handled directly by AI summaries, diminishing the immediate click value of such content categories.
This paradigm shift necessitates a re-evaluation of content priorities:
- Deprioritizing “Thin” or Easily Summarized Content: Content that merely regurgitates definitions or provides generic answers to common FAQs is increasingly vulnerable to being fully digested by AI overviews. The return on investment for such content is diminishing as users receive satisfactory answers directly on the SERP. Instead, valuable content must offer more than just basic information.
- Focus on Original Research and Proprietary Data: Content providers are increasingly investing in generating unique information that AI models cannot simply synthesize from existing sources. This includes conducting original surveys, experiments, case studies, or presenting proprietary datasets. Such content becomes highly authoritative and defensible against AI summarization, often serving as a primary source that AI *must* cite, driving increased trust and potentially direct traffic for deeper engagement.
- In-depth Guides, Tutorials, and Experiential Content: A HubSpot survey found that web strategists are planning significant investments in how-to guides (45%) and in-depth reviews/comparisons (37%)[27]. These content formats inherently require more detailed analysis, step-by-step instructions, or personal experience that a brief AI summary cannot fully convey. Users engaging with such queries often demonstrate a deeper intent and are more likely to click through for comprehensive understanding or application.
- Thought Leadership and Unique Perspectives: AI can summarize facts, but it struggles with generating genuine thought leadership, critical analysis, or nuanced opinions. Content that embodies a distinctive viewpoint from a recognized expert or organization stands out. This type of content further reinforces E-E-A-T signals, making it more appealing to human readers and more likely to be recognized as authoritative by search algorithms.
- Interactive and Multimedia Content: Beyond text, content that offers interactive tools, calculators, rich visualizations, or high-quality multimedia (videos, podcasts) provides a user experience that AI summaries cannot replicate. These elements foster deeper engagement and give users compelling reasons to visit the originating website.
- E-E-A-T Fortification: Every piece of content should be meticulously crafted to signal strong Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. This involves prominent author bios, clear editorial guidelines, rigorous fact-checking, references to credible sources, and showcasing any awards or certifications. The goal is to make the human element and credibility undeniable.
The table below summarizes the shift in content strategy focus in the AI era:
| Traditional SEO Content Focus | AI-Era SEO Content Focus (2026) |
|---|---|
| Basic FAQs and Definitions | Original Research, Proprietary Data |
| Generic Informational Articles | In-Depth Guides, How-Tos, Tutorials |
| Commoditized Content (easy to replicate) | Experiential Content (personal stories, reviews) |
| Keyword-stuffed for rankings | Thought Leadership, Unique Perspectives |
| Volume-based content production | Quality-driven, E-E-A-T Fortified Content |
| Text-heavy, often thin content | Interactive, Multimedia-Rich Content |
By 2026, the mantra for content creators will be to produce content that is either *deeply useful, uniquely original, or inherently experiential*, making it resilient to disintermediation by AI summaries and ensuring it continues to drive value, whether through direct clicks or enhanced brand visibility and authority. This transition moves content marketing away from a purely quantitative approach towards a more qualitative, human-centric one.
Technical SEO and AI: New Protocols and Ethical Considerations
While the preceding discussions focused on content, AI’s influence extends deeply into technical SEO. The emergence of AI crawlers, the increasing importance of structured data, and debates around content licensing are shaping new technical considerations for achieving optimal visibility and protecting intellectual property.
Key aspects include:
- Structured Data (Schema Markup): The rise of conversational AI and enhanced AI summaries has magnified the importance of structured data. Clear, precise schema markup (e.g., FAQPage, HowTo, Q&A, Article, Product schemas) helps search engines and AI models accurately understand the context and specific entities within a page. This improves the likelihood of a page’s content being used in direct answers, rich snippets, or AI overviews. By 2026, the meticulous implementation of relevant schema will be non-negotiable for any content aspiring to AI visibility.
- Voice Search and Conversational Query Optimization: As users increasingly interact with AI through voice assistants and conversational interfaces, the nature of queries is shifting. Queries are becoming longer and more natural-language based. Data from Google Ads between 2022 and 2024 showed a near doubling in the volume of searches that were 7-8 words long after ChatGPT’s debut[23]. While shorter queries (<4 words) still dominate the majority of Google searches, a significant trend towards “answer-seeking” questions is observable[24]. Technical SEO must reflect this by optimizing for more natural language, long-tail, and question-based keywords. Content should be structured to provide direct, concise answers to potential voice queries.
- AI Crawler Management: A significant technical and ethical debate centers around AI crawlers (e.g., OpenAI’s GPTBot, Google-Extended). Publishers are increasingly concerned about these bots scraping their content to train AI models without explicit consent or compensation. In response, some content providers are using `robots.txt` files to block specific AI crawlers, asserting control over their data’s usage. By 2026, standards for AI crawler management are likely to be more formalized, potentially including specific new metadata directives (like `noai` or similar tags) that allow webmasters to signal their preferences for AI training data use. Navigating these emerging protocols will be a crucial technical SEO task, balancing discoverability by legitimate search crawlers with protection against unauthorized AI data ingestion.
- Content Licensing and Syndication: The legal landscape surrounding AI’s use of copyrighted web content remains fluid, as exemplified by lawsuits against Google from publishers like Penske Media Corporation (owner of *Rolling Stone*) alleging unlawful scraping[13]. Conversely, proactive partnerships, such as those between the Associated Press and OpenAI[25] or News Corp and Time Magazine with OpenAI[26], demonstrate a move towards compensated content licensing. Technical SEO teams may need to work closely with legal and business development teams to implement systems for content fingerprinting, usage tracking, and potential integration with syndicated content feeds tailored specifically for AI platforms, ensuring proper attribution and monetization.
- Analytics for AI Impressions: Traditional analytics tools are primarily designed to track clicks. As AI answers reduce click-throughs but increase “impressions” within the SERP (e.g., content being cited in an AI summary), there’s a growing need for new measurement methodologies. By 2026, SEO analytics tools will likely offer more sophisticated tracking for AI-derived visibility, providing insights into when, where, and how content is utilized by AI models, even without a direct referral click.
The technical aspects of SEO in the AI era are rapidly expanding beyond traditional site speed and crawlability. They now encompass intelligent content structuring, nuanced crawler management, proactive content licensing considerations, and new analytical frameworks to measure visibility in an increasingly AI-driven search ecosystem.
Conclusion to Section 4
The relentless march of AI into content generation and search mechanics has irrevocably altered the digital landscape for 2026. The internet is awash with AI-generated content, pushing content saturation to unprecedented levels and intensifying competition for visibility. While AI tools have become indispensable for streamlining SEO workflows and enhancing efficiency, the sheer volume of mediocre, machine-produced text necessitates a critical emphasis on human quality control. Google’s unwavering focus on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) stands as the primary bulwark against the degradation of search results. As zero-click searches become the norm, driven by AI summaries, marketers are compelled to redefine “visibility” beyond mere clicks, focusing on being cited, structured for generative AI optimization, and creating deeply valuable, original, and experiential content that AI cannot fully replicate. The technical underpinnings also shift, requiring sophisticated implementation of schema, adaptation for conversational queries, and strategic management of AI crawlers. Ultimately, the AI-generated content deluge has transformed SEO from a game of quantity to one of unparalleled quality, authenticity, and human value.
The next section will delve into the profound impact of AI on user search behavior and expectations, exploring how conversational AI and personalization are reshaping the search journey for consumers and businesses alike.
5. Evolving SEO Strategies in the AI Era
The advent of artificial intelligence, particularly generative AI, has irrevocably altered the landscape of search engine optimization (SEO). What was once a relatively linear path of optimizing for keywords and backlinks has fractured into a multi-faceted discipline, demanding adaptability and strategic foresight. As of 2026, the core tenets of discoverability remain, but the methods, metrics, and even the fundamental philosophy of SEO have undergone a profound transformation. This section delves into the critical shifts defining contemporary SEO – from optimizing for AI summaries to reinventing content creation, and from adapting success metrics to mastering the technical nuances required for AI visibility. The overriding challenge for SEO professionals is to navigate a world where search engines increasingly aim to answer queries directly, thus reducing traditional website traffic, while simultaneously offering new avenues for brand visibility and engagement within the AI-powered search experience.
Optimizing for AI Visibility: The Rise of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
In the wake of generative AI’s integration into search engines, a new paradigm for visibility has emerged: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). This concept directly addresses the phenomenon of “zero-click searches,” which have surged to nearly 60% of Google searches by 2024, up from approximately 50% in 2018[1][2]. In the EU, this figure is similar, at 59.7% of searches ending without a click[3]. The proliferation of AI-powered answer summaries on the search results page now satisfies a significant proportion of user queries directly at the source, foregoing the need to click through to external websites[4]. This shift has profound implications, forcing SEOs to consider how content can achieve prominence not just in traditional organic listings, but within these AI-generated summaries.
A key finding from March 2025 indicated that when Google’s AI Overview appeared, users clicked traditional search results roughly half as often (8% clickthrough rate versus 15% without AI)[5]. Furthermore, in 26% of searches where an AI summary was present, users took no further action at all, compared to 16% in classic search results[6]. This data underscores a critical challenge: even a #1 organic ranking may yield less traffic if an AI answer sufficiently addresses the user’s query. Consequently, optimizing for AI visibility means strategically positioning content to be cited or summarized by AI models.
The foundational elements of GEO include:
- Structured Data Optimization: Implementing comprehensive and accurate schema markup is more crucial than ever. Schema.org tags for FAQs, HowTo articles, Q&A sections, and product information help AI models understand the context and intent of content, making it easier for them to extract and present relevant information in summaries[7]. This ensures machine readability and increases the likelihood of content being chosen as a source.
- Semantic SEO and Comprehensive Coverage: AI models excel at synthesizing information from various sources to provide a complete answer. Therefore, content strategies must prioritize semantic SEO, aiming for comprehensive coverage of topics rather than merely optimizing for individual keywords. This involves answering related questions, addressing sub-topics, and building topical authority around specific subjects. Such thoroughness signals to AI models that the content is a valuable and authoritative resource[8].
- Building Source Credibility and Authority: AI models, like traditional search algorithms, are designed to prioritize trustworthy and authoritative sources. Pew Research Center found that 88% of AI summaries cited three or more sources, with Wikipedia, Reddit, and YouTube frequently appearing as top cited sources[9]. To be recognized as a valuable source by AI, websites must cultivate robust E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals. This involves showcasing author credentials, providing clear citations, and maintaining a strong reputation within the respective industry or topic. Google’s Helpful Content updates, which launched in 2022 and were more fully integrated into the core ranking system by March 2024, explicitly favor content that is helpful, reliable, and created by people, for people, over content designed solely for search engines[11].
- Monitoring AI Mentions: Akin to tracking keyword rankings or organic traffic, SEO professionals are increasingly monitoring instances where their content or brand is cited within AI summaries. While dedicated analytics tools for “assistant mentions” are still evolving, the ability to track brand visibility within AI-generated responses (e.g., through Google Search Generative Experience, Bing Chat footnotes) is becoming a critical aspect of measuring success in this new landscape[8]. By 2026, such metrics are expected to be standard in comprehensive SEO reporting.
Redefining Success Metrics Beyond Traditional Clicks
The traditional SEO success metric of “organic click-through rate” (CTR) and direct website traffic is undergoing a fundamental re-evaluation. With the rise of zero-click searches and AI summaries, brands must broaden their definition of visibility and impact. As publishers lament “dramatically” declining web traffic and some pursue legal action over lost visibility[12][13], SEO professionals are compelled to adapt their measurement frameworks.
Google insists that AI features create “new opportunities” and that overall web traffic hasn’t significantly dropped[14], reporting 1.5 billion+ monthly users engaging with AI search experiences by early 2025[15]. While Google also maintains it sends “billions of clicks” to sites daily[16], the observable trend of increasing zero-click searches necessitates a more nuanced approach to measuring success. This redefinition includes:
- Brand Visibility and Impression Share in AI Answers: If an AI summary directly answers a user’s query while prominently citing a brand as the source, this still generates significant brand value, even without a direct click. It functions as a brand impression, thought leadership positioning, and implicit endorsement from the search engine. New success metrics are emerging, such as “assistant mentions” or “share of voice in AI results,” to quantify this type of visibility[8].
- Engagement with Interactive SERP Features: As search results become more dynamic and interactive, success metrics extend beyond clicks to include engagement with elements like embedded videos, carousels, maps, or interactive tools directly on the search engine results page (SERP). An SEO strategy might prioritize being featured in these elements, understanding that while they may not drive direct traffic, they can influence user behavior deeper in the funnel.
- Conversion on the SERP: For certain types of queries, particularly local or direct-answer queries, the goal may not be a click to a website but a direct action on the SERP itself, such as a phone call, getting directions, or booking an appointment through a Google Business Profile listing. Optimizing for these direct conversions becomes a valid metric of success.
- Quality of Referral Traffic: While the volume of AI-driven traffic remains relatively small (just 0.15% of global web traffic as of mid-2025)[17], it is growing rapidly, up over 7x from 2024[18]. Notably, visitors referred by AI assistants tend to be highly engaged, spending approximately 68% more time on sites than organic search visitors[19]. This highlights the importance of quality over quantity; even fewer clicks can be more valuable if they lead to deeper engagement and higher conversion rates.
By 2026, SEO reports are expected to feature a blend of traditional metrics (keyword rankings, organic traffic volume, CTR) alongside AI-era metrics (AI answer citations, SERP feature impressions, engagement with interactive results, and quality of AI-referred traffic), painting a holistic picture of search performance.
| Traffic Type | Global Web Traffic Share (Mid-2025)[17] | Engagement Rate Compared to Organic Search[19] | Growth Rate (YoY from 2024)[18] |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Referral Traffic | 0.15% | 68% longer time on site | 7x growth |
| Google Search Traffic | ~45% (dominant source) | Baseline | Stable/Declining for some (publishers) |
Table 1: Comparison of AI Referral Traffic vs. Google Search Traffic Metrics (Mid-2025)
Adapting Content Strategies for Engagement and Originality
The AI era demands a fundamental re-evaluation of content strategy. With AI models capable of generating vast amounts of text, and search engines leveraging these models to provide direct answers, the value proposition of generic or “thin” content has plummeted. Half of new online articles were written by AI in late 2025, and an Ahrefs study in April 2025 found 74% of newly created web pages contained AI-generated text, of which 71.7% were a human-AI mix and 2.5% were fully AI-written[21][23]. This deluge creates a heightened need for content that stands out through genuine human insight, originality, and depth[21].
Key adaptations in content strategy include:
- Prioritizing Unique and Deeply Useful Content: If an AI can efficiently summarize basic facts, the incentive to create simple FAQ or definitional content diminishes. Instead, SEOs are now focusing on content types that AI is less equipped to produce. A HubSpot survey in late 2024 found that web strategists planned greater investments in “how-to guides” (45%) and “in-depth reviews/comparisons” (37%), alongside thought leadership pieces[25]. These formats offer clear, actionable value that often requires human experience and specialized knowledge.
- Original Research and Experiential Content: Content featuring original research, proprietary data, case studies, or firsthand experiences is highly valued. AI models, while adept at synthesizing existing information, cannot easily generate truly novel insights or data. By investing in and publishing original research, brands can become indispensable sources for both human users and AI models, making their content less susceptible to cannibalization.
- E-E-A-T-Driven Content Creation: Google’s emphasis on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is more critical than ever. Content should clearly demonstrate the author’s credentials, real-world experience, and a deep understanding of the subject matter. This can involve author bios, editorial guidelines that enforce expert review, and showcasing the unique perspective that a human can bring. The fact that 93% of marketers still review and edit AI-generated content before publishing underscores the ongoing need for human oversight to ensure accuracy and “helpfulness”[27].
- Optimizing for Conversational and Long-Tail Queries: The rise of conversational AI (like ChatGPT) has led to users framing queries in more natural, question-like language. Google Ads data from 2022-2024 shows a nearly 2x jump in searches that are 7-8 words long since ChatGPT’s debut[29]. While shorter queries still dominate, the trend toward more specific, answer-seeking questions means content should be structured to directly address these complex queries, often through distinct question-and-answer sections.
- Human-AI Collaboration in Content Creation: Businesses are increasingly adopting a hybrid approach where AI accelerates content production, but human expertise refines and enriches it. While 87% of content marketers use AI for content creation in some capacity, 93% manually review and edit AI-generated content[27]. This involves using AI for tasks like keyword clustering, topic outlining, first drafts, or summarizing, freeing human writers to focus on adding unique perspectives, deep analysis, and creative storytelling that resonate with readers and distinguish them from purely machine-generated output.
Growing Significance of Technical SEO: Schema, AI Crawler Management, and Core Web Vitals
Technical SEO, always a cornerstone, has gained renewed importance in the AI era. As search engines and AI models become more sophisticated, the clarity and accessibility of website data are paramount for optimal visibility. Ensuring that content is easily discoverable, crawlable, and understandable by intelligent agents is no longer just about rankings but about becoming a reliable source for AI summaries and answers.
- Enhanced Schema Markup and Structured Data: Implementing a wide array of Schema.org markup is essential for AI-driven search. This includes not only basic organization and article markup but also more specific types like:
FAQPage: For clearly structured questions and answers frequently asked content, which AI can readily pull for direct answers.HowTo: For step-by-step instructions, making content easily digestible for both users and AI summaries describing processes.QAPage: For question-and-answer formatted content, aiding AI in identifying relevant snippets.Product: For detailed product information, crucial for e-commerce, though AI typically refers less traffic here (product pages received <0.5% of AI referral clicks in one analysis)[31], robust data ensures potential visibility and accurate information dissemination.ReviewandAggregateRating: For user-generated content and trust signals, which AI models consider when evaluating source credibility.
This detailed markup helps AI models interpret the context of information on a page, making it more likely to be featured in generative search experiences, featured snippets, or rich results.
- AI Crawler Management and Content Licensing: A significant technical and ethical challenge is managing how AI bots crawl and use website content. Publishers are increasingly concerned about AI models ingesting their proprietary content without fair compensation or clear attribution, leading to lawsuits, such as the one filed by Penske Media (owner of Rolling Stone) against Google in July 2025, alleging unlawful scraping and summarization of journalism[33]. In response, some organizations are adopting strategies for AI crawler management:
- Robots.txt Directives: Websites can use their robots.txt file to block specific AI crawlers (e.g., OpenAI’s GPTBot) from accessing their content. This allows publishers to control which AI models can train on their data.
- Emerging `noai` Directives: The industry is exploring new metadata directives, akin to `noindex` or `nofollow`, such as a `noai` tag, which would explicitly communicate to AI crawlers not to use specific content for training or summarization purposes. This could become a standard by or before 2026.
- Content Licensing Agreements: A more proactive approach involves striking licensing deals with AI companies. The Associated Press (AP) famously signed a two-year agreement with OpenAI in July 2023, allowing OpenAI to license AP’s news archives for model training in exchange for compensation and access to OpenAI’s technology[35]. Other major publishers like News Corp and Time Magazine followed suit in 2024[37]. For SEOs, this means understanding how technical measures can protect intellectual property while also exploring new revenue streams for high-quality, proprietary content.
- Core Web Vitals and Page Experience: While not directly AI-specific, the importance of Core Web Vitals (CWV) and overall page experience remains high. Google’s algorithms continue to prioritize user experience, and fast, stable, and visually appealing websites are more likely to rank well. This indirectly impacts AI visibility, as high-ranking, user-friendly pages are often preferred as sources for AI summaries. Ensuring excellent CWV (Largest Contentful Paint, Cumulative Layout Shift, First Input Delay) and mobile-friendliness indirectly feeds into a site’s overall authority and eligibility for AI citations.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: As AI-powered voice search and other assistive technologies become more prevalent, optimizing for accessibility ensures that content is consumable across a wide range of devices and for users with diverse needs. Proper use of ARIA attributes, image alt text, and semantic HTML contributes to a more inclusive web and improves the ability of AI models to understand and process content.
The technical SEO landscape in 2026 is one where granular control over how AI interacts with content is paramount, alongside maintaining the foundational principles of user experience and machine readability. These technical considerations are integral to securing and maintaining visibility in an AI-driven search ecosystem.
The AI era is not merely a technological upgrade but a paradigm shift in how information is discovered and consumed. SEO professionals, traditionally focused on driving clicks, must now embrace a broader understanding of “visibility” that includes presence within AI-generated summaries and interactive SERP features. This requires a strategic pivot towards generating deeply valuable, original content, meticulously structuring data for AI consumption, and redefining success metrics beyond traditional traffic. As Google continues to iterate on its AI search capabilities through 2026 and beyond, the SEO community’s ability to adapt to these evolving dynamics will dictate success.
The next section will delve deeper into the specific industry-wide impacts and responses to AI, exploring how different sectors are navigating this complex shift and what opportunities and challenges lie ahead.

6. Industry-Specific Impacts and Adaptations
The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in search and content generation has not created a uniformly distributed impact across all online sectors. Rather, its effects are nuanced, producing a complex tapestry of challenges and opportunities that vary significantly by industry. While some sectors, particularly those rich in informational content, find themselves becoming primary sources for AI summaries, others, such as e-commerce, face distinct hurdles in maintaining traditional traffic flows. Media publishers, in particular, are grappling with what some have termed a “traffic apocalypse,” necessitating fundamental shifts in their operational and monetization strategies. Understanding these industry-specific dynamics is crucial for any business seeking to navigate the evolving search landscape of 2026 and beyond. This section delves into how different sectors are being reshaped by AI in search, examining the mixed outcomes for informational sites and blogs, the emergent challenges for e-commerce and product-related searches, and the strategic recalibrations underway among news and media publishers. Finally, it touches upon the implications for local businesses, underscoring the need for tailored adaptation strategies in the face of pervasive AI integration.
6.1. Informational Sites and Blogs: A Double-Edged Sword of Visibility
Informational websites, including blogs, how-to guides, and Q&A forums, are experiencing a dual impact from AI in search. On one hand, their content often serves as the essential raw material for AI Overviews and generative AI summaries within search results. This places them in a position of authority, with their insights directly informing the answers presented to users. On the other hand, this direct summarization by AI frequently leads to a reduction in clicks to the original source, paradoxically decreasing direct website traffic even as their information gains wider AI-driven exposure.
6.1.1. The AI’s Preferred Sources: Prominence Amidst Reduced Clicks
A Pew Research Center report from July 2025 indicated that when Google’s AI Overview presented a summary, the click-through rate (CTR) to traditional search results dropped from 15% to 8%1. An even more striking statistic revealed that in 26% of searches featuring an AI summary, users took no further action at all, compared to 16% for traditional results2. This phenomenon, which contributes to the nearly 60% zero-click rate in Google searches by 20243, means that while informational sites might be extensively referenced by AI, that citation does not always translate into direct visits.
However, being cited by AI still carries significant weight. The same Pew Research report noted that major informational platforms like Wikipedia, Reddit, and YouTube were among the most frequently cited sources in Google’s AI summaries4. These platforms, known for their comprehensive, user-generated, or expert-curated content, illustrate the type of information AI models are trained to prioritize for authoritative answers. This prominence can bolster a site’s authority and recognition, even if direct traffic metrics fall. For instance, finance and tech sites receive a disproportionately large share of AI-driven traffic compared to other sectors5, indicating that deeply analytical and specialized informational content is highly valued by AI models.
6.1.2. Adaptation Strategies for Informational Sites
To thrive in this environment, informational sites and blogs are adopting various strategies to maintain engagement and value beyond a simple AI summary.
* **Creating Un-summarizable Content**: Sites are shifting away from generic FAQs that can be easily answered by AI. Instead, they focus on producing content that offers depth, unique perspectives, and experiential value that AI struggles to replicate. This includes original research, intricate case studies, detailed tutorials, and subjective thought leadership. As one HubSpot survey found, web strategists plan to invest heavily in how-to guides (45%) and in-depth reviews/comparisons (37%)6. This content aims to hook users with value propositions that require a click-through for full understanding, even if an AI provides an initial overview.
* **Emphasizing Interactivity and Community**: Since AI primarily delivers static information, informational sites are enhancing their offerings with interactive tools, rich multimedia (videos, infographics), and strong community features (comment sections, forums). These elements provide reasons for users to visit the actual site, fostering deeper engagement and potentially converting passive information seekers into active participants.
* **Adapting to Conversational Queries**: The rise of conversational AI means search queries are becoming longer and more specific. Queries of 7+ words have nearly doubled since ChatGPT’s debut7. Informational sites are optimizing for these natural language queries, ensuring their content directly addresses complex questions and provides detailed, nuanced answers that align with AI-driven search patterns. This includes leveraging FAQ schema markup and structuring content to clearly answer discrete questions that AI models might extract.
* **The Stack Overflow Conundrum**: The experience of Stack Overflow serves as a cautionary tale for niche informational sites. The popular Q&A forum for developers saw a 13.9% year-on-year traffic decline in March 20238. This drop coincided with the rise of AI tools like ChatGPT and GitHub’s CoPilot, which could instantly generate code snippets and answers that developers previously sought on the forum. Stack Overflow responded by temporarily banning AI-generated answers and later by developing its own AI-powered features, OverflowAI, to summarize and contextualize its vast knowledge base. This demonstrates that even highly specialized informational platforms must proactively integrate AI or risk disintermediation, and that emphasizing curated, expert-verified answers is paramount.
In conclusion, informational sites and blogs find themselves in a strategic balancing act. While being a primary source for AI-generated answers provides a new form of visibility and authority, maintaining direct traffic and user engagement requires a deliberate shift towards content depth, interactivity, and unique value propositions that transcend simple summarization.
6.2. E-commerce and Product Search: Navigating the “Traffic Desert”
The e-commerce sector faces a particularly acute challenge with the rise of AI in search. Unlike informational content, product pages and online storefronts rarely benefit directly from AI-generated summaries. AI models tend to provide recommendations or summarize product features rather than directing users straight to transactional pages, creating what could be termed a “traffic desert” for direct e-commerce referrals.
6.2.1. Minimal Direct AI Referral Traffic
One of the most concerning statistics for e-commerce comes from a late-2024 study, which found that product and e-commerce pages received an alarmingly low **<0.5%** of AI referral clicks9. This contrasts sharply with blog and article pages, which accounted for 77.3% of clicks from AI platforms like ChatGPT and Bard10. This data clearly indicates that AI tools are not primarily designed to send users directly to shopping listings. When consumers ask an AI about “the best laptop under $1000,” the AI might synthesize a list of recommendations, often without providing direct links to purchase pages, or only linking to reviews rather than product detail pages. This challenges the traditional e-commerce SEO model, which relies on direct organic search traffic to product categories and individual listings.
6.2.2. Strategic Shifts for E-commerce SEO
Given this landscape, e-commerce businesses are compelled to adapt their SEO and content strategies to ensure visibility within the AI-dominated search environment.
* **Content Marketing for Discovery**: Instead of solely optimizing product pages, e-commerce brands are heavily investing in informational content that AI models are more likely to reference. This includes:
* **Buying Guides**: Comprehensive articles comparing products, explaining features, and offering purchase advice (e.g., “Beginner’s Guide to DSLR Cameras”).
* **Comparison Charts and Reviews**: Detailed analyses of different products within a category, often incorporating expert opinions and user testimonials.
* **How-to Content**: Articles explaining how to use products, solve problems with them, or integrate them into a lifestyle (e.g., “How to Choose the Right Coffee Machine for Your Home”).
This strategy aims to capture user attention earlier in their purchase journey, during the research phase, where AI is more likely to provide summaries that include brand mentions or conceptual information relating to their products.
* **Optimizing for Conversational Commerce**: With the increase in natural language queries and voice search, e-commerce businesses are looking to integrate their catalogs and product information directly into AI assistants and conversational interfaces. This means providing structured data (schema markup) that clearly outlines product attributes, pricing, and availability so that AI models can accurately answer specific questions posed by users. Partnerships with AI search providers like Microsoft Bing or integration with platforms like Meta AI to feed product data are becoming increasingly relevant.
* **Enhanced Product Data and Feeds**: Beyond traditional on-page SEO, focusing on robust product data feeds is critical. This ensures that even if an AI doesn’t direct a user to a specific product page, it accurately represents the product’s details in its summary. Rich, well-structured product data can make a brand’s offerings more discoverable and presentable within AI-generated responses.
* **Local SEO for Bricks-and-Mortar E-commerce**: For retailers with physical stores, local SEO remains vital. AI overviews often pull from Google Maps and Google Business Profile data for local queries. Ensuring accurate and enriched business listings (photos, reviews, descriptions, opening hours) helps present compelling information to users, even if they don’t click through to the website. While zero-click search could increase for local queries, users often still click for transactional details like directions or booking.
* **Focus on Post-Click Experience**: When a rare AI-referred click does occur, or when users eventually reach an e-commerce site through other means, the site experience becomes paramount. Highly engaged visitors from AI platforms spend 68% longer on sites than those from traditional Google search11. This suggests that while AI traffic volume is low, its quality is high. E-commerce sites must therefore focus on optimizing their user experience, conversion paths, and site speed to capitalize on these valuable, albeit fewer, AI-driven visits.
In essence, e-commerce SEO in 2026 demands a dual approach: a robust content marketing strategy that generates informational authority for AI consumption, coupled with meticulous product data management and an exceptional on-site experience to convert the engaged users that trickle through.
6.3. Media Publishers: Facing a “Traffic Apocalypse” and Strategic Diversification
No industry has expressed more alarm about the impact of AI on search visibility than news and media publishers. The summary-providing nature of generative AI in search results directly threatens their core business model, which relies heavily on page views for advertising revenue. What began as a creeping concern has intensified into what some publishers describe as a “traffic apocalypse.”
6.3.1. The Erosion of Referral Traffic
Publishers have witnessed significant declines in search referral traffic throughout 2024–2025. Wired’s editor-in-chief, Gideon Lichfield, publicly lamented a “traffic apocalypse” (a phrase echoed by Axios, warning of a “Google Zero” scenario where Google sends “zero” meaningful traffic to publishers)12. The primary mechanism for this decline is Google’s AI Overviews, which summarize news, articles, and other content directly on the SERP, obviating the need for users to click through to a publisher’s site.
The data supports this concern: when an AI summary is present, the likelihood of a user clicking a traditional search result halves, from 15% to 8%1. Added to this, sources cited within AI summaries (e.g., news articles) do not always receive prominent attribution or a direct click. Publishers argue that Google is effectively using their costly-to-produce content to generate its own answers, thereby siphoning off their audience and associated advertising revenue. This sentiment fueled lawsuits, such as the one filed by Penske Media Corporation (owner of *Rolling Stone*) against Google in July 2025, alleging unlawful scraping and summarization of journalism13. The lawsuit claimed that Google was using publishers’ content for AI without compensation, harming their revenue streams14, highlighting the adversarial stance many publishers feel compelled to adopt. The timing of this lawsuit, following reports of “dramatically” declining web traffic attributed to AI answers15, underscores the severity of the issue for these organizations.
6.3.2. Diversification and New Monetization Models
In response to these existential threats, media publishers are no longer solely dependent on Google for audience acquisition strategies. They are implementing aggressive strategies to diversify their revenue streams and cultivate direct audience relationships.
* **Subscription Models**: A push towards paid subscriptions for premium content is a key defensive move. By offering exclusive articles, in-depth analysis, or ad-free experiences, publishers aim to convert casual readers into loyal, paying subscribers, thereby insulating themselves from erratic search traffic fluctuations.
* **Direct Audience Channels**: Newsletters, dedicated mobile applications, and hosted events are becoming central to audience engagement strategies. These channels allow publishers to build direct relationships with their readership, gather first-party data, and reduce reliance on third-party platforms for distribution. Axios notes that many media companies are investing in newsletters, apps, and events businesses to hedge against search traffic losses16.
* **Content Licensing Deals**: A more collaborative, albeit controversial, approach involves licensing content directly to AI developers. The Associated Press (AP) set an early precedent in July 2023 by signing a two-year agreement with OpenAI, allowing its news archives to be used for model training in exchange for compensation and access to OpenAI’s technology17. By mid-2024, other major players like News Corp (publisher of *The Wall Street Journal*) and Time Magazine also followed suit, striking content licensing deals with OpenAI and Google18. These agreements represent a nascent model where news content is syndicated to AI platforms, potentially securing revenue and controlled credit for publishers when their stories are summarized.
* **Technical Measures and Policy Engagement**: Publishers are exploring technical solutions, such as implementing `robots.txt` rules to block specific AI crawlers (e.g., OpenAI’s GPTBot) or using content fingerprinting to identify unauthorized use of their material. Simultaneously, they are actively engaging in legal and policy discussions around intellectual property rights and fair compensation for AI’s use of copyrighted content. The outcome of lawsuits and industry negotiations will likely shape new standards for how AI models access and credit web content by 2026.
The shift for media publishers is profound, moving from a primarily advertising-driven, volume-based traffic model to one emphasizing direct reader relationships, premium content, and strategic partnerships with AI entities. SEO for news organizations is evolving to involve closer collaboration with legal and business development teams to protect and monetize intellectual property in the age of AI.
6.4. Local and Service Businesses: Adapting to AI-Driven Micro-Moments
Local and service-oriented businesses face a distinct set of challenges and opportunities shaped by AI, particularly through the lens of zero-click searches and conversational AI. While the direct financial impact might not be as dramatic as in media, the need for precise, AI-interpretable information is paramount.
6.4.1. Zero-Click Risks and Opportunities for Local Queries
Local search has always benefited from direct, intent-driven queries (e.g., “restaurants near me,” “plumber in [city]”). However, AI’s ability to directly answer these questions without requiring a click poses a new challenge. For example, if a user asks, “Find me a 24-hour pharmacy nearby,” an AI could potentially present the necessary information (name, address, phone number) directly on the SERP or via a voice assistant, circumventing a visit to a business’s website. Google’s AI Overviews frequently pull from Google Maps and Google Business Profile (GBP) data for such queries. This means that a business’s visibility in an AI-driven local search is heavily dependent on the quality and completeness of its GBP listing.
However, local searches often involve implied transactional intent, such as getting directions, making a reservation, or calling directly. These actions still necessitate interaction beyond a mere summary, creating an ongoing opportunity for local businesses to convert AI visibility into tangible outcomes.
6.4.2. Strategies for Local SEO in the AI Era
Local and service businesses need to refine their tactics to ensure they remain discoverable and actionable within an AI-first search environment.
* **Mastering Google Business Profile (GBP)**: Optimizing GBP listings is more critical than ever. This includes:
* **Comprehensive and Accurate Information**: Ensuring business name, address, phone number, operating hours, and services are correct and up-to-date.
* **Rich Media**: Uploading high-quality photos and videos that showcase the business.
* **Active Review Management**: Encouraging customer reviews and responding promptly to both positive and negative feedback, as reviews are a strong signal of trustworthiness and quality that AI models can leverage.
* **Service and Product Listings**: Utilizing GBP’s features to list specific services or products offered, complete with descriptions.
* **Voice Search Optimization**: As conversational AI becomes more prevalent, optimizing for natural language and voice queries is crucial. This means businesses should consider how users might *speak* their queries (e.g., “What’s a good Italian restaurant in downtown Boston?” instead of “Italian restaurant Boston”). Content on websites, especially FAQs, should be structured to answer common questions in a conversational style that aligns with voice search patterns (e.g., “Do you offer vegan options?” for a restaurant).
* **Schema Markup**: Implementing local business schema markup on websites helps search engines and AI models understand key information about the business, such as its type, location, contact details, and reviews. This structured data makes it easier for AI to extract and present accurate information in direct answers.
* **Hyper-local Content Strategy**: Creating blog posts or landing pages that target ultra-specific local queries (e.g., “best dog park in [specific neighborhood],” “emergency auto repair near [specific landmark]”) can help capture niche search intent that AI might still direct to a local establishment for more details or action.
* **Conversion-Focused Websites and Booking Systems**: Since users may still click through for transactional purposes, a frictionless on-site experience is vital. Easy-to-use online booking systems, clear calls-to-action (CTAs) for phone calls, and mobile-responsive designs are essential to convert AI-referred users who are ready to make a decision.
The AI-driven search landscape demands that local and service businesses go beyond basic listings, embracing comprehensive digital presence management and content strategies tailored for conversational and zero-click interactions, while always retaining a focus on the customer’s final intent to act or transact.
6.5. Conclusion: Diverse Impacts, Unified Need for Adaptation
The industry-specific analyses reveal that while AI’s influence on search visibility and SEO is universal, its manifestation and the necessary adaptive strategies are highly varied. From informational sites grappling with the paradox of increased visibility but reduced traffic, to e-commerce struggling with minimal direct AI referrals, and media publishers facing what feels like an existential threat, each sector must chart its own path forward. Local businesses, too, must sharpen their digital presence for a world of zero-click answers.
The overarching theme across all industries is the imperative to adapt content strategy. Generic, easily summarizable content will increasingly be consumed directly by AI, leaving businesses vying for attention. Success in 2026 will hinge on producing content that is either uniquely valuable, deeply experiential, highly specialized, or designed for direct action beyond simple information retrieval. Furthermore, optimizing for AI extends beyond traditional SEO, encompassing “Generative AI Optimization”—ensuring content is structured and authoritative enough to be cited by AI models, tracking AI-derived impressions, and engaging proactively with platforms and policy.
The evolving landscape also underlines a growing tension between content creators and AI platforms regarding fair use and monetization. Hybrid models of content licensing and new attribution standards are likely to emerge as the industry seeks a sustainable balance. For all sectors, staying agile, experimenting with new content formats, and meticulously analyzing user behavior in the age of AI will be critical for maintaining and growing search visibility. The shift is not just tactical; it’s strategic, demanding a re-evaluation of what SEO truly means in a world where AI increasingly mediates access to information.
Moving forward, understanding the technological underpinnings of this transformation is equally important. The subsequent section will delve into the technical SEO considerations and emerging tools that are shaping how websites interact with AI-powered search engines.
—
1 References
- Pew Research Center. (2025, July 22). Google users are less likely to click on links when an AI summary appears.
- Pew Research Center. (2025, July 22). Google users are less likely to click on links when an AI summary appears.
- Search Engine Land. (2024, July 2). Nearly 60% of Google searches end without a click in 2024.
- Pew Research Center. (2025, July 22). Google users are less likely to click on links when an AI summary appears.
- Search Engine Journal. (2024, December 22). Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market.
- HubSpot Blog. (2024, November 5). The Future of Google: How AI Overviews could impact traffic (survey).
- Search Engine Land. (2024, December 16). How search query length is shifting in the LLM era: Insights for brands.
- Similarweb Blog. (2023, April 19). Stack Overflow is ChatGPT casualty: Traffic down 14% in March.
- Search Engine Journal. (2024, December 22). Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market.
- Search Engine Journal. (2024, December 22). Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market.
- SE Ranking Study. (2025, August 27). AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Platforms.
- Axios. (2025, July 23). Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock.
- Axios. (2025, September 15). Publishers shift AI ire to Google.
- Axios. (2025, September 15). Publishers shift AI ire to Google.
- Axios. (2025, September 15). Publishers shift AI ire to Google.
- Axios. (2025, July 23). Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock.
- Axios. (2023, July 13). AP strikes news-sharing and tech deal with OpenAI.
- AP News. (2024, May 23). OpenAI to start using news content from News Corp.. Axios. (2024, June 27). Time strikes licensing deal with OpenAI.
7. Emerging Partnerships and Future Outlook
The dawn of generative AI in search has undeniably reshaped the relationship between content creators, technology platforms, and consumers. As AI models increasingly mediate access to information, extracting and synthesizing content directly on the search results page, traditional revenue models and visibility strategies for publishers have been profoundly disrupted. This disruption has catalyzed a pivotal shift from outright competition and legal disputes to a nascent era of strategic partnerships and collaborative frameworks. By 2026, the digital landscape is poised to see an acceleration of these trends, characterized by innovative content licensing agreements, the development of industry standards for attribution, and the emergence of new symbiotic models between AI developers and content producers. This section delves into the evolving dynamics of these partnerships, forecasting the trajectory of content usage, monetization, and ethical considerations in an AI-driven search ecosystem.
7.1. From Conflict to Collaboration: The Rise of AI Content Licensing
The initial response from many content creators, particularly news publishers, to the proliferation of AI-generated summaries was one of alarm and legal contention. By mid-2025, publications like Wired described the situation as a “traffic apocalypse,” attributing significant declines in web traffic to AI search features that provided answers directly on the search results page, thereby reducing click-through rates to external websites[12]. Pew Research Center data from March 2025 indicated that when Google’s AI-generated summaries appeared, users clicked traditional result links only 8% of the time, compared to 15% without an AI summary. Furthermore, 26% of searches with an AI answer resulted in no further user action, signaling direct answer satisfaction[2]. Such statistics fueled legal challenges, exemplified by Penske Media Corporation (owner of *Rolling Stone*) filing a high-profile lawsuit against Google in July 2025, alleging unlawful scraping and summarization of journalism, leading to siphoned traffic[13]. This legal action highlighted the growing tension over intellectual property rights and fair compensation for content creators.
However, alongside these conflicts, a more pragmatic approach began to emerge: direct content licensing agreements. These agreements represent a critical pivot from confrontation to collaboration, acknowledging the inevitable integration of AI into information retrieval while seeking to establish equitable terms for content usage. The genesis of this trend can be traced back to 2023, when the Associated Press (AP) signed a pioneering two-year licensing agreement with OpenAI. This groundbreaking deal permitted OpenAI to use portions of AP’s vast news archives to train its large language models (LLMs), in exchange for compensation and access to OpenAI’s technology[11]. AP’s proactive stance was driven by the recognition that AI systems were already ingesting news content, making a collaborative approach more beneficial than futile resistance. This foresight earned AP praise for setting a precedent for adaptation rather than opposition.
Following AP’s lead, the trend gained significant momentum. By mid-2024 and extending into 2025, several other major publishers, including News Corp (publisher of the Wall Street Journal) and Time Magazine, entered into similar content licensing deals with OpenAI and Google[14]. These agreements typically involve publishers receiving payment for licensing their content to AI developers, often coupled with access to AI tools or insights. The primary objective for publishers in these arrangements is to offset the revenue losses incurred from declining referral traffic and reduced ad impressions, ensuring the economic viability of quality journalism and content creation in the AI era. For AI developers, these partnerships provide access to high-quality, authoritative, and fact-checked data, which is crucial for training and refining their models, reducing the risk of “hallucinations” or inaccuracies that can plague models trained on less curated web data.
The table below summarizes some key characteristics and motivations behind these emerging content licensing agreements:
| Stakeholder | Motivations for Partnership | Expected Outcomes (by 2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Content Publishers (e.g., AP, News Corp, Time) |
|
|
| AI Developers (e.g., OpenAI, Google) |
|
|
By 2026, it is projected that such collaborations will become standard practice, moving beyond initial reactive measures to forming a fundamental component of the digital content economy. This will likely lead to more sophisticated pricing models for content licensing, potentially tiered based on the volume, recency, and exclusivity of the data provided.
7.2. Evolving Models for Content Usage and Attribution
The rise of content licensing agreements is intrinsically linked to the parallel need for established industry standards for content usage and attribution in the AI-driven search landscape. While licensing provides a commercial framework, the technical and ethical implementation of how AI models consume, synthesize, and present information — and critically, how they attribute it — remains a complex challenge. The current state, where Google’s AI summaries cite multiple sources (88% of AI summaries cite three or more sources)[1], is a step towards attribution, but often insufficient for satisfying publishers’ needs for traffic and brand recognition.
A key projection for 2026 is the further development of dynamic and layered attribution models. Simply listing source URLs at the bottom of an AI summary might not suffice for publishers struggling with declining web traffic. New models could involve more prominent in-summary citations, interactive elements that allow users to easily delve deeper into source material, or even direct integration of publisher-branded content within AI-generated responses (e.g., an AI chatbot suggesting “For a detailed analysis, read this article by [Publisher Name]”)[11]. Such integrations would not only credit the original creator but also funnel high-quality, engaged traffic back to the source, particularly for complex queries where an AI summary may not fully satisfy user intent.
Another area of rapid evolution will be the technical mechanisms for content control and identification. Publishers are increasingly exploring methods to manage how AI crawlers interact with their content. This includes using `robots.txt` directives to block specific AI bots (like OpenAI’s GPTBot) or implementing new metadata standards. For instance, the use of `noai` directives or content fingerprinting technologies could become commonplace by 2026. These aim to give publishers greater control over whether their content is used for AI training, and to track unauthorized usage, creating leverage in licensing negotiations. For SEO professionals, understanding and implementing these evolving technical specifications will be crucial, ensuring their content is discoverable by legitimate AI systems that honor attribution, while potentially excluding malicious or uncompensated scraping.
Transparency in AI’s content sourcing is also expected to become a cornerstone of industry standards. As AI becomes more deeply embedded in search, users will demand to know the provenance of the information they receive. This includes not just visible citations but potentially more detailed insights into the training data used, the recency of the information, and the reliability scores assigned to source publishers by the AI algorithm. This increased transparency could foster greater trust in AI-generated content and empower users to seek out original sources when needed.
The development of these standards will likely be a collaborative effort involving:
- AI Developers: To build and integrate attribution features into their models and interfaces.
- Publishers & Content Creators: To advocate for robust attribution and fair compensation mechanisms.
- Industry Bodies & Associations: To formulate best practices and common protocols for content usage, much like existing standards for sitemaps or schema markup.
- Regulators: To potentially introduce legislation if industries fail to establish equitable frameworks, particularly concerning copyright and intellectual property in the age of AI.
7.3. Collaborative Models Beyond Licensing: Industry Symbiosis
Beyond simple licensing agreements, 2026 is expected to witness the emergence of more deeply integrated, symbiotic collaborative models between AI developers and content producers. These models aim to create mutual value, moving beyond a transactional exchange for data to strategic partnerships that redefine how information is created, distributed, and consumed.
7.3.1. AI-Assisted Content Creation
AI’s role in content creation is already significant, with studies in 2025 finding that 50-70% of new online content is at least partially AI-generated[8], and 86% of SEO professionals integrating AI into their workflows[7]. While this has led to a “content flood,” it has also driven publishers to seek human-AI collaboration that enhances quality rather than simply boosting quantity. By 2026, AI developers may offer advanced tools and APIs to publishers, allowing them to:
- Automate research and data synthesis: AI can quickly aggregate and summarize background information for journalists, freeing them to focus on unique angles and investigative work.
- Personalize content delivery: AI can help publishers tailor news digests or article recommendations to individual user preferences, increasing engagement and potentially subscription rates.
- Translate and localize content at scale: Opening up new global markets for publishers.
- Generate dynamic content formats: Such as interactive summaries or audio versions of articles, enhancing accessibility and user experience.
The Associated Press’s initial deal with OpenAI, which provided AP with access to OpenAI’s technology, hints at this deeper integration[11]. This enables publishers to use AI not just as a consumer of their content but as a powerful assistant in its creation and distribution.
7.3.2. Revenue Sharing and Federated Search
As AI answers satisfy more queries directly, advertisers may shift budgets from traditional search engine result page (SERP) ads to opportunities within AI interfaces. This could lead to revenue-sharing models where publishers receive a portion of ad revenue generated when their content is featured or implicitly consumed within AI summaries. Alternatively, a “federated search” model could emerge, where AI platforms don’t just summarize content but actively integrate search results from various publisher networks directly into their responses. This could offer a more seamless experience for users and a more direct referral path for content creators, bypassing the traditional Google SERP entirely.
7.3.3. Specialized AI Models and Vertical Search
The impact of AI on search visibility is not uniform across all sectors. Informational content, such as blog posts and how-to guides, currently accounts for a disproportionately large share of AI referral clicks (77.3% in a late-2024 study)[10], while e-commerce pages receive less than 0.5%[10]. This divergence could foster partnerships focused on domain-specific AI models. For example, a travel publisher might collaborate with an AI developer to create a specialized travel-planning AI that draws exclusively from the publisher’s vetted content, offering a more authoritative and deep experience than a general-purpose AI. Similarly, in fields like finance and technology, where sites already receive an outsized portion of AI-driven traffic, tailored solutions could emerge to provide highly specialized, real-time insights drawn from specific, licensed content sources[10]. This would represent a departure from generic web search towards more curated, vertical AI search experiences.
7.4. The Future of Standards: A New Digital Compact
By 2026, the cumulative effect of these emerging partnerships and evolving usage models will necessitate a new “digital compact” between content creators and AI platforms. This compact will likely entail:
- Universal Attribution Standards: Beyond simple links, a standardized metadata scheme or API for robust, machine-readable attribution that clearly indicates the original source, authorship, and licensing terms.
- Opt-Out and Opt-In Mechanisms: Clearer, globally recognized technical and legal frameworks for content creators to either opt-out their content from AI training or opt-in for specific, compensated usage.
- Ethical AI Content Guidelines: Jointly developed guidelines to address issues such as content manipulation, the responsible use of AI-generated content (e.g., disclaimers for AI-assisted articles), and preventing the spread of misinformation via AI.
- Dispute Resolution Frameworks: Established pathways for addressing violations of licensing agreements, copyright infringement, or attribution failures, potentially through industry-led arbitration or standardized legal processes.
The shift towards a collaborative future is driven by a mutual understanding: AI platforms need high-quality, authoritative content to be genuinely useful and trustworthy, while content creators need sustainable models to continue producing such content in an AI-dominated information environment. The legal pressures and economic realities of 2024-2025 have paved the way for these necessary alliances. While challenges certainly remain, the trajectory for 2026 points towards a more integrated and, hopefully, more equitable ecosystem where AI and human-generated content can coexist, each enriching the other.
This dynamic interplay of emerging partnerships, evolving attribution standards, and new collaborative models underscores the profound transformation underway in the search and content industries. For practitioners in SEO and digital strategy, staying attuned to these developments will not merely be an advantage but a necessity for designing resilient and effective strategies in a rapidly evolving digital world.
8. Key Statistics and Data Analysis
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has ushered in a transformative era for search engine visibility and Search Engine Optimization (SEO). To comprehensively understand this profound impact and anticipate its trajectory towards 2026, a rigorous examination of key statistical data and emerging trends is essential. This section aggregates and analyzes critical quantitative insights drawn from recent studies and industry reports, shedding light on shifts in user behavior, market dynamics, content creation, and SEO practices. From the dramatic rise of zero-click searches driven by AI-powered summaries to the explosive adoption of AI tools by consumers and marketers alike, the data paints a picture of a search ecosystem in flux. By dissecting these numbers, we aim to provide a robust, evidence-based foundation for strategic planning in the evolving digital landscape.
The Phenomenon of Zero-Click Searches and AI’s Role
Perhaps the most disruptive trend identified in recent years is the surge in “zero-click searches,” where users find answers directly on the search engine results page (SERP) without navigating to an external website. This phenomenon has been significantly accelerated by the integration of generative AI into search experiences.
Escalating Zero-Click Rates
In 2024, nearly 60% of Google searches in the U.S. terminated without a single click to an organic or paid result[1]. This figure represents a considerable increase from approximately 50% in 2018[2], indicating a steady and accelerating trend. In the EU, the situation is remarkably similar, with 59.7% of searches yielding no clicks to the open web[3]. This means that for the majority of queries, Google’s SERP features—including knowledge panels, featured snippets, and increasingly, AI-powered answer summaries—are sufficient to satisfy user intent.
The implications for website owners are profound. A #1 ranking, traditionally the pinnacle of SEO success, now faces a challenge where direct traffic is no longer guaranteed, even if the content is deemed the most relevant. The primary driver behind this latest acceleration is unequivocally the rise of AI-powered answer summaries. These summaries, often appearing at the top of the SERP, synthesize information from various sources to provide a direct answer to the user’s query.
AI Summaries: Halving Click-Through Rates
When Google’s AI Overview (or similar AI-generated summary) is displayed on a search page, the impact on traditional click-through rates (CTR) is stark. A Pew Research Center report from March 2025 revealed that users clicked a traditional result link only 8% of the time when an AI summary was present[4]. This is a dramatic reduction compared to the 15% CTR observed on pages without an AI summary[4].
Furthermore, the study highlighted that in 26% of searches where an AI answer appeared, users took no further action, effectively ending their search journey on Google’s platform[5]. This is significantly higher than the 16% of sessions ending without a click on traditional search results page[5]. Such data quantifies the direct erosion of outgoing traffic to publishers and content creators, prompting concerns from various sectors.
Table 8.1: Impact of AI Summaries on Click-Through Rates (March 2025)
| Search Result Type | Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Searches ending without action |
| :————————————— | :———————– | :—————————– |
| Traditional Search Results (No AI Summary) | 15%[4] | 16%[5] |
| With AI Summary | 8%[4] | 26%[5] |
This data provides concrete evidence that AI summaries are, in many cases, satisfying user queries directly, thereby curtailing the need to click through to source websites. Publishers have vocally expressed their alarm, attributing “dramatically” declining web traffic to these direct answers and some are even pursuing legal action over perceived lost visibility and content scraping[6],[7]. Google, while maintaining that AI features create “new opportunities” and that overall web traffic has not significantly dropped, is nevertheless expanding AI in search, rolling out AI summaries to approximately 18% of U.S. Google queries by early 2025 and reporting over 1.5 billion monthly users engaging with AI search experiences[8],[9].
This escalating zero-click environment indicates a profound strategic pivot for SEO; merely ranking high is no longer enough. The focus must broaden to maximizing visibility *within* the SERP itself, whether that means optimizing for featured snippets that AI might draw from, or ensuring brand mentions within AI overviews, even if a direct click is sacrificed.
User Adoption and Market Share Dynamics in the Age of AI
The rapid emergence of generative AI tools like ChatGPT has not only reshaped how information is presented but also how users seek it, leading to shifts in adoption patterns and, to a lesser extent, market share.
Explosive Uptake of Conversational AI Tools
OpenAI’s ChatGPT demonstrated unprecedented growth upon its launch in 2023, attracting 100 million users within a mere two months[10]. This made it the fastest-adopted consumer application in history. By March 2023, the platform was already garnering 1.6 billion visits per month, even momentarily surpassing Bing in global traffic volume[11]. This astronomical leap signaled a fundamental change in how a significant portion of the online population intended to interact with digital information.
Consumer appetite for AI tools in search-like tasks continued to grow into 2024-2025. A February 2025 U.S. survey indicated that 71.5% of Americans had tried AI search tools like ChatGPT or Bing Chat at least occasionally[12]. This adoption is particularly pronounced among younger demographics, with 82% of Gen Z reporting having used AI search, compared to 45% of Baby Boomers[13].
Despite this high awareness and experimentation, traditional search engines have maintained their dominant position for general queries. The same survey found that 79.8% of users still prefer Google or Bing for most queries[14]. Furthermore, only 14% of users reported using AI search daily[14]. This suggests that while AI tools are widely explored, they are largely complementary to traditional search rather than a direct replacement as of late 2025. Initial studies found that AI chatbots accounted for only about 3% of total search volume in 2024[15].
Bing’s AI-Driven Market Share Movement
Microsoft’s integration of GPT-4 into Bing in early 2023 served as a high-profile experiment in AI-enhanced search. This move initially generated significant interest, leading Bing to break the 100 million daily active users milestone[16] and doubling its U.S. monthly active users in Q2 2023[17]. However, this curiosity bump translated into only a marginal, albeit notable, increase in overall market share. By late 2023, Bing’s global search share reached approximately 3.4%, up from roughly 3.0% pre-AI integration[18].
While this represented growth for a long-stagnant competitor, it pales in comparison to Google’s enduring dominance. Google still handles over 20 times more queries, with around 460 million U.S. daily visits compared to Bing’s 13.8 million at its 2023 peak[19],[16]. The consensus remains that while AI can stimulate user interest, it has not yet Dethroned Google, which benefits from deeply entrenched user habits and cross-platform ecosystem advantages.
Table 8.2: Search Engine Market Share Comparison (Late 2023)
| Search Engine | Global Market Share | U.S. Daily Visits (Estimate) | Key AI Integration |
| :———— | :—————— | :————————— | :—————– |
| Google | ~90% | ~460 million[19] | AI Overviews, SGE, Gemini |
| Bing | ~3.4%[18] | ~13.8 million[19] | GPT-4 integration |
The data indicates that while AI search tools are here to stay and their adoption rates are impressive, traditional search preference remains strong. For SEOs, this means a dual approach: maintaining robust SEO for Google while also exploring optimization for AI-powered search engines and standalone chatbots, recognizing the latter’s high growth potential and varying user engagement models.
The Deluge of AI-Generated Content and SEO Implications
The accessibility and efficiency of generative AI platforms have led to an unprecedented increase in the volume of online content, fundamentally altering the competitive landscape for visibility.
AI’s Contribution to New Web Content
By late 2025, a significant portion of newly created online articles are estimated to be authored by AI, with some analyses placing this figure at over 52% of all new online articles each month[20]. Digging deeper, a study of 900,000 newly created webpages in April 2025 found that 74.2% contained some degree of AI-generated content[21]. A breakdown revealed that 71.7% were a human-AI mix, 2.5% were fully AI-written, and only 25.8% consisted entirely of human-written text[22].
This dramatic influx of content, much of which is generated or assisted by AI, has profound SEO implications. It signifies a rise in basic, functional content, leading to heightened competition for visibility. Search algorithms are evolving to detect and devalue low-quality, mass-produced content, necessitating a renewed focus on genuine helpfulness and originality.
Marketers’ Swift Adoption of AI for SEO
SEO professionals have rapidly embraced AI, leveraging its capabilities to streamline workflows and enhance efficiency. Approximately 86% of SEO professionals have integrated AI into their strategic approaches[23]. Key applications include keyword research, competitor analysis, content outlining, and generating meta descriptions and titles.
The efficiency gains are substantial: 75% of marketers report that AI helps cut down time spent on routine SEO tasks[24]. This increased productivity is translating into tangible results, with 65% of businesses reporting better SEO outcomes with AI assistance[25], and 52% of SEO pros noting improved on-page performance after deploying AI tools[26].
However, the widespread use of AI for content generation has underscored the critical importance of human oversight. A striking 93% of marketers still meticulously review and edit AI-generated content before publication[27]. This highlights an industry-wide recognition that raw AI output often lacks the nuance, accuracy, and “helpfulness” required for high-quality, high-ranking content. Google’s March 2024 Helpful Content update reinforced this, integrating the algorithm into its core ranking systems to penalize “unhelpful” content and reward authoritative, human-friendly material[28],[29].
Table 8.3: SEO Professionals’ AI Adoption & Impact (2025)
| Statistic | Value | Source |
| :————————————– | :—————————————- | :———- |
| SEO professionals using AI | 86%[23] | SeoProfy |
| Marketers reducing time on SEO tasks via AI | 75%[24] | SeoProfy |
| Businesses seeing better SEO results with AI | 65%[25] | SeoProfy |
| SEO pros reporting improved on-page performance via AI | 52%[26] | SeoProfy |
| Marketers reviewing AI-generated content | 93%[27] | SeoProfy |
| New webpages with AI-generated content | 74.2%[21] | Ahrefs |
| Fully AI-written new webpages | 2.5%[22] | Ahrefs |
| Human-AI mix new webpages | 71.7%[22] | Ahrefs |
| New articles authored by AI/month (est.) | >52%[20] | Brussels Times |
The data emphasizes that while AI boosts content volume and SEO efficiency, a quality-first approach, coupled with human expertise and rigorous editing, is paramount to success in a content-saturated web. This dynamic ensures that E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) remains a cornerstone of effective SEO heading into 2026.
Shifting Search Queries and Referral Traffic Patterns
AI’s influence extends beyond content creation and zero-clicks, fundamentally altering how users phrase their queries and how third-party sites receive traffic.
Queries Becoming Longer and More Conversational
The rise of conversational AI interfaces has prompted a subtle but significant shift in user query patterns. Instead of terse keyword strings, users are increasingly comfortable posing longer, more specific, and question-style searches. Data from Google Ads between 2022 and 2024 shows a nearly twofold increase in queries of seven words or more following ChatGPT’s debut[30]. Examples include complex, specific questions like, “How much is car insurance for a 2022 Honda Accord in Ohio?” By 2026, experts anticipate a continued leaning towards natural language, intent-focused queries.
However, Google’s data also suggests that the majority of searches still consist of shorter phrases, with only about 10% of queries currently exceeding seven words[31]. This indicates a gradual evolution rather than an abrupt overhaul of search behavior, but one that necessitates SEO adaptation towards long-tail, semantic, and question-based keyword strategies.
Evolving Referral Traffic from AI Platforms
While the volume of traffic referred from AI search tools to external websites remains small, its growth rate and user engagement characteristics are highly significant. As of mid-2025, all AI chat platforms combined contributed a mere 0.15% of global web traffic[32]. To put this in perspective, Google alone still drives 300 times more traffic than all AI tools combined[33]. Even in the most impacted industries, AI referrals constituted only about 0.25% of total traffic[34].
However, this nascent channel is experiencing exponential growth, increasing over sevenfold from 2024 to 2025[32]. Some sectors have witnessed extraordinary jumps of 400-900% in AI-driven visits in a single quarter[35]. Crucially, users referred from AI platforms exhibit highly engaged behavior: they spend an average of 68% longer on-site compared to visitors from traditional Google search results[36].
These “high-intent” visitors represent a valuable segment, suggesting that even small volumes of AI referral traffic can yield disproportionately positive outcomes, particularly for conversions or deeper content engagement. Some businesses are already experiencing positive traffic outcomes, with 41% of web strategists reporting an increase in website traffic since Google launched AI summaries in late 2024, compared to 17% who saw declines[37]. Forecasting forward, if current growth rates persist, AI-driven visits could account for 10-20% of site traffic in certain sectors by 2026[38].
Variable Impact Across Industries and Content Types
AI referral traffic does not benefit all content types or industries equally:
- Informational Content Dominant: LLM-based search heavily favors informational content. A late 2024 study showed that 77.3% of clicks originating from AI tools (ChatGPT, Bard, etc.) went to blog or article pages[39]. News articles accounted for only 8%, and guide-style content less than 3%[39].
- E-commerce Disadvantage: Product and e-commerce pages received a strikingly low <0.5% of AI referral clicks in one analysis[40]. AI tools tend to summarize product categories or provide recommendations rather than directing users to specific product listings, posing challenges for retailers.
- Sector-Specific Gains: Finance and tech sites, in particular, appear to capture an outsized portion of AI-driven traffic, with these industries jointly accounting for a huge share of AI-sourced visits[41]. This is likely due to the informational nature of many queries in these fields.
This uneven distribution means that SEO strategies must be highly tailored. Informational content, thought leadership, and original research are positioned to potentially gain valuable, highly engaged referral traffic from AI platforms. Conversely, e-commerce sites need to rethink their approach, perhaps by enhancing informational content around products or integrating directly with AI shopping interfaces.
New Models for Content & Revenue: Publisher Responses
The demonstrable impact of AI on search visibility is forcing publishers and content creators to re-evaluate their fundamental business models and relationships with search platforms.
Publishers Grappling with Traffic Declines
Major online publishers have reported significant search traffic declines throughout 2024-2025. This downturn is attributed, in part, to Google’s AI Search Generative Experience (SGE), which provides direct answers, reducing the need for users to click to external sites. The editor-in-chief of Wired famously termed this a “traffic apocalypse” for online media[42]. Other news sites have also reported their traditional search referral traffic is “quickly evaporating”[43].
This scenario has prompted news organizations to diversify their revenue streams, with some investing heavily in subscriptions, newsletters, apps, and other direct audience engagement channels to hedge against dwindling search traffic[44],[45]. The ultimate fear among publishers is a “Google Zero” scenario where Google sends negligible traffic to their sites[46], making their IP visible in AI summaries but without corresponding traffic or revenue.
Emergence of AI-Content Licensing Partnerships
In response to the evolving landscape, some content providers are proactively engaging with AI companies through licensing agreements. The Associated Press (AP) led this charge by signing a two-year licensing deal with OpenAI in 2023, allowing ChatGPT to use AP’s news content for training in exchange for compensation and access to OpenAI’s technology[47]. By mid-2024, other prominent publishers, including News Corp (owner of The Wall Street Journal) and Time Magazine, followed suit, striking similar content licensing deals with OpenAI and Google[48],[49].
These agreements signal a potential new paradigm where content creators are compensated for the use of their intellectual property by AI models. This emerging model aims to mitigate revenue losses from reduced referral traffic by establishing direct financial relationships with AI developers. By 2026, such partnerships are expected to become more widespread, fostering an ecosystem where quality, authoritative content is directly valued by AI platforms, rather than solely through ad-driven traffic. This also implies that SEO will increasingly need to consider content’s value as “training data” and explore strategies for “generative AI optimization” to ensure content is appropriately cited or directly monetized.
The analysis of these key statistics and data points underscores a dynamic and challenging period for SEO. While traditional search remains dominant, the rapid ascension of zero-click SERPs, AI-powered summaries, and new conversational AI platforms demands strategic adaptation. Businesses must focus on creating high-quality, authoritative content that provides tangible value, optimizing for visibility within the AI-enhanced SERP, and potentially exploring new partnership models with AI developers. The coming years will undoubtedly see an acceleration of these trends, making agile, data-driven SEO strategies more crucial than ever.
The next section will delve into the methodological approaches employed in this research, detailing how these insights were gathered and analyzed.
9. Frequently Asked Questions
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into search engines and the broader digital landscape has catalyzed a myriad of questions for businesses, marketers, and content creators alike. As we approach 2026, the initial ripples of AI’s impact have grown into significant waves, reshaping how information is sought, found, and consumed. This section addresses the most common and pressing questions regarding the influence of AI on search visibility and Search Engine Optimization (SEO), distilling complex trends into actionable insights. From the potential for AI to displace traditional search engines like Google to the nuances of optimizing content for a new algorithmic reality, understanding these FAQs is crucial for navigating the evolving digital environment.
Will AI Replace Google as the Primary Search Engine?
The short answer, as of 2026, appears to be: not yet, but it’s a rapidly evolving landscape often complementing traditional search rather than fully replacing it. While AI chatbots and search experiences have seen explosive growth and adoption, Google maintains a dominant position, a testament to its long-standing user habit and comprehensive ecosystem.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT, for instance, reached 100 million users within just two months of its 2023 launch, marking it as the fastest-growing consumer application in history at the time[5]. By March 2023, ChatGPT was attracting an astonishing 1.6 billion visits per month, even momentarily surpassing Bing in global traffic[11]. This rapid adoption signifies a powerful user inclination towards conversational AI for information retrieval.
A U.S. survey in February 2025 indicated that a substantial portion of the population – 71.5% of Americans – had already experimented with AI tools for search, yet a significant majority, 79.8%, still expressed a preference for traditional search engines for most of their queries[4]. This suggests that while consumers are keen to explore AI’s capabilities, they haven’t entirely abandoned the familiar architectures of Google or Bing for their everyday search needs. Only 14% of users reported using AI search daily, further emphasizing its current supplementary role[4].
Demographic data reveals a clear generational divide in AI adoption for search. Gen Z, for example, shows an 82% adoption rate for AI search, starkly contrasting with the 45% among Baby Boomers[4]. This generational gap suggests that while older demographics are slower to integrate AI into their search habits, younger users are rapidly embracing these new tools, potentially foreshadowing future shifts in search behavior.
Microsoft’s efforts to challenge Google’s dominance provide a valuable case study. After integrating GPT-4 into Bing in 2023, Bing experienced a temporary surge in interest, breaking the 100 million daily active user mark for the first time[NOTABLE-1], and seeing its U.S. monthly active users double in Q2 2023[14]. However, this boost translated into only a marginal increase in global market share, with Bing’s share rising from approximately 3.0% to 3.4% by late 2023[14]. In comparison, Google continues to process over 20 times more queries, with an estimated 460 million daily visits in the U.S., significantly overshadowing Bing’s peak of 13.8 million daily visits in 2023[4].
While AI chatbots now account for a notable share, estimated around 3% of global search volume in 2024[6], this remains a fraction compared to traditional search. The consensus among experts is that by 2026, AI-driven search will predominantly serve as a complement to, rather than a replacement for, classic search engines. The growth rates for AI tools are undeniably high, indicating a persistent upward trend, but Google’s established user base, robust features, and seamless integration across its vast ecosystem continue to cement its position as the primary gateway to online information. SEO strategies must therefore account for presence in both traditional search engines and emerging AI platforms.
How Can Content Be Optimized for AI Answers and Generative AI Search?
Optimizing content for AI answers and generative AI search, often termed “Generative AI Optimization” (GAIO), represents a significant evolution in SEO strategy. With the rise of AI Overview features in Google and answers provided by chatbots, it’s no longer solely about ranking #1 in organic results but also about ensuring content is digestible and quotable by AI models.
- Focus on Authority and Trust: AI models are increasingly trained on high-quality, authoritative sources to minimize “hallucinations” and provide reliable information. Platforms like Wikipedia, Reddit, and YouTube were identified as among the most frequently cited sources in Google’s AI summaries, indicating a preference for established and often community-vetted content[10]. To optimize, content creators must prioritize E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) by demonstrating real-world expertise, citing credible sources, and establishing a reputable brand presence.
- Semantic SEO and Comprehensive Topic Coverage: AI excels at understanding the nuances of language and context. Therefore, moving beyond keyword stuffing to cover topics comprehensively and semantically is crucial. This involves answering related questions, addressing sub-topics, and providing context that traditional keyword matching might miss. The goal is to become an indispensable resource for a given topic, increasing the likelihood of AI models drawing from your content for broad questions.
- Structured Data and Schema Markup: Implementing schema markup (e.g., FAQPage, HowTo, Q&A schema) helps search engines and AI models understand the content’s structure and purpose. This makes it easier for AI to extract specific answers, lists, or steps to present in summaries. Well-structured data can directly influence how your content appears in rich snippets and, by extension, how AI summarizes it.
- Clarity, Conciseness, and Direct Answers: AI summaries thrive on clear, direct answers to questions. While comprehensive content is important, ensuring that key questions are answered concisely and early in the text makes it easier for AI to extract and present this information. Think about providing a “TL;DR” (Too Long; Didn’t Read) summary or a prominent answer section for common queries.
- Original Research and Unique Insights: As AI fills the web with more generic content, original research, proprietary data, unique case studies, and distinct thought leadership become vital differentiators. AI is less equipped to generate truly novel insights or conduct primary research, making content with these elements more valuable and likely to be cited. Businesses should invest in content that AI cannot easily replicate, such as in-depth reviews, comparative analyses, and experiential pieces[49].
- Monitoring AI Mentions and Adaptability: It’s becoming increasingly important to track when and how your brand or content is cited in AI summaries and responses. This might involve setting up alerts for brand mentions within AI contexts. Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), for example, highlights sources within its AI overviews, offering a new form of attribution. Being adaptable and responsive to how AI evolves and how user behavior shifts in response will be key to long-term optimization.
A recent Ahrefs study in April 2025 found that 74.2% of newly created web pages contained some form of AI-generated content[8]. While only 2.5% were fully AI-written, 71.7% were a human-AI mix[8]. By late 2025, over half (52%) of all new online articles were estimated to be authored by AI[9]. This content explosion necessitates a strategic approach where quality, uniqueness, and human oversight (93% of marketers still review and edit AI-generated content[8]) are paramount to cut through the noise and appeal to both human users and sophisticated AI models. Google’s Helpful Content updates continue to penalize “unhelpful, low-value” content, reinforcing the need for quality over pure AI-driven quantity.
What Will Happen to Traditional Search Visibility in 2026?
The concept of “traditional search visibility”—meaning organic listings that drive direct clicks to websites—is undergoing a profound transformation. While it won’t disappear entirely, its nature and impact are changing significantly, largely due to the rise of AI-powered answer summaries and zero-click searches.
The Rise of Zero-Click Searches: A critical trend is the accelerating rate of zero-click searches. In 2024, nearly 60% of Google searches in the U.S. ended without a click to an external website[3]. This figure is up from approximately 50% in 2018[1] and is projected to continue its ascent through 2026 with the increased prevalence of generative AI in search. In the EU, the trend is similar, with 59.7% of searches resulting in zero clicks[2]. This phenomenon is largely driven by Google’s ability to provide direct answers through featured snippets, Knowledge Panels, and, more recently, AI-generated overviews. When Google’s AI Overview appears on a search results page, users click traditional result links roughly half as often (8% click-through rate versus 15% without an AI summary)[1]. Furthermore, in 26% of searches where an AI summary is present, users take no further action at all, compared to 16% on classic results pages[1]. This data unequivocally points to a substantial diversion of traffic that previously flowed from search engines to external websites.
Impact on Publishers and Content Creators: Publishers and content creators who historically relied on organic search traffic are feeling the brunt of this shift. Major online publishers have reported significant declines in search referral traffic throughout 2024–2025[11]. Wired’s editor-in-chief, for instance, referred to a “traffic apocalypse” due to falling referrals from both Facebook and Google[11]. The potential for a “Google Zero” scenario, where Google sends almost no meaningful traffic to publishers, is a stark warning for content producers[11]. This situation is prompting publishers to explore alternative revenue models, such as subscriptions, newsletters, apps, and events, to reduce their dependence on search engines[11].
| Scenario | Traditional Link Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Zero-Click Rate |
|---|---|---|
| With AI Summary | 8%[1] | 26%[1] |
| Without AI Summary (Traditional Results Only) | 15%[1] | 16%[1] |
Redefining “Visibility”: While direct clicks may decrease for certain query types, visibility itself will take on new forms. Being cited within an AI summary, even without a direct click, can serve as a powerful branding impression and establish thought leadership. Forward-thinking SEO professionals are starting to measure “assistant mentions” or “share of voice in AI answers” as new key performance indicators. This necessitates optimizing for content that AI models will confidently reference, such as highly authoritative, well-structured, and unique content.
Google’s Adaptation: Google, while disputing some of the more dire predictions about traffic declines, is actively iterating on its AI features. It insists that AI creates “new opportunities” and that it still sends “billions of clicks” to websites daily[6]. Google’s Helpful Content updates and algorithmic refinements aim to reward trustworthy, human-friendly content, implying a pushback against the mass production of low-value AI-generated content[7]. By 2026, Google is expected to continue fine-tuning its algorithms to balance user satisfaction with the health of its content ecosystem, potentially offering publishers more nuanced controls or even revenue-sharing models for AI-generated snippets of their content.
In conclusion, traditional search visibility as solely measured by direct organic clicks will diminish for many types of queries by 2026. However, it will not vanish. Instead, the focus for SEO will shift to a more holistic approach: ensuring content is highly discoverable, authoritative enough to be cited by AI, provides unique value to warrant a click-through when AI answers suffice, and is optimized for both traditional search and emerging AI platforms. The game is changing from a pure click-driven model to a more complex interplay of impressions, citations, and engaged user journeys.
What Are the Best Practices for Optimizing Content for AI in 2026?
Optimizing content for AI in 2026 requires a significant paradigm shift from traditional SEO, emphasizing not just machine readability but also human-centric value and trustworthiness. Here are the best practices:
- Prioritize E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): Google’s quality ranking signals place immense importance on E-E-A-T. This is amplified in the age of AI. Content that demonstrates verifiable experience (e.g., from personal use, case studies), deep expertise (written or reviewed by subject matter experts), clear authoritativeness (reputable sources, strong backlinks), and trustworthiness (accuracy, transparency, positive user reviews) will be favored by both Google’s algorithms and AI models. Ensure author bios are prominent, credentials are highlighted, and content is fact-checked rigorously.
- Create Deeply Helpful and Unique Content: With AI capable of generating vast amounts of generic information, the premium on truly helpful, unique, and insightful content is higher than ever. Shift focus from basic FAQs that AI can easily summarize to content that offers:
- Original Research: Surveys, studies, proprietary data that doesn’t exist elsewhere.
- In-depth Guides and Tutorials: Step-by-step instructions, complex problem-solving that requires human nuance. HubSpot’s 2024 survey showed “how-to guides” (45%) as a top planned content investment[49].
- Experiential Content: Personal stories, genuine reviews, comparative analyses that reflect real experience.
- Thought Leadership: Unique perspectives, analyses of industry trends, and forward-looking insights.
This content serves as a “click-through magnet” even if an AI provides a summary, as users will often seek more depth or different perspectives.
- Implement Advanced Structured Data (Schema Markup): Schema helps AI understand the context and components of your content. Beyond basic article schema, focus on:
FAQPage: For clearly structured questions and answers.HowTo: For sequential steps in a process.Q&A: For forum-style content or distinct question-answer pairs.- Specific industry schemas (e.g.,
Product,Recipe,Event).
This enables AI to accurately extract and present information from your site.
- Optimize for Conversational and Long-Tail Queries: The rise of voice search and AI chatbots encourages users to employ more natural language and longer, more specific questions. Studies show queries of 7+ words have nearly doubled since ChatGPT’s debut[23]. Tailor content to answer these complex, multi-part questions directly. Use natural language in headings, subheadings, and introductory paragraphs.
- Content Structure for Scannability and Extractability:
- Use clear, descriptive headings (H1, H2, H3).
- Employ bullet points, numbered lists, and tables for easy information digestion by both humans and AI.
- Write concise introductions and summaries that capture the main point.
- Ensure answers to common questions are easily identifiable within the text.
- Source Attribution and Linking: While AI may summarize, it often cites its sources. By being a frequently cited source for high-quality information, you build overall domain authority and brand recognition. Promote transparency by clearly citing your own sources within your content, further establishing trustworthiness.
- Consider “Generative Engine Optimization” (GAIO): Actively monitor if and how your content is being used by AI assistants and generative search experiences. Tools that show AI-derived impressions or mentions will become crucial. This new form of optimization means understanding how AI consumes and presents information to users, and adapting your content to perform well within that framework.
- Human Oversight and Refinement of AI-Generated Content: If utilizing AI for content creation, manual review and editing are indispensable. About 93% of marketers currently review and edit AI-generated content before publishing[7]. This ensures accuracy, quality, and originality, preventing penalties from Google’s “Helpful Content” system[8] and maintaining brand reputation.
- Technical SEO for AI Crawlers: Be aware of and manage AI crawler access. Some publishers are using robots.txt to block AI crawlers (like GPTBot) if they don’t wish their content to be used for AI training without consent or compensation. Conversely, explicitly allowing certain AI crawlers might be beneficial for inclusion in specific AI-powered services.
By integrating these practices, businesses and content creators can position themselves effectively for search visibility in 2026, navigating the increasingly complex interplay between human users, traditional search engines, and sophisticated AI models.
What Are the Long-Term Implications for Businesses Reliant on Organic Search Traffic?
For businesses heavily reliant on organic search traffic, the long-term implications of AI integration are profound and necessitate strategic adaptation. The era of focusing solely on organic clicks from classical search results is giving way to a more multifaceted and nuanced approach to digital visibility.
- Diversified Traffic Strategies are Imperative: The sustained increase in zero-click searches (nearly 60% in 2024[3]) and the halving of click-through rates when AI overviews appear[1] mean that exclusive reliance on traditional organic search is an increasingly risky proposition. Businesses must diversify their traffic acquisition channels, including:
-
- Direct Traffic and Brand Building: Strong brand recognition encourages users to seek out your site directly, bypassing search engines altogether.
- Email Marketing and Newsletters: Building an owned audience can create a reliable traffic stream that is independent of algorithm changes.
- Social Media Engagement: Cultivating communities and driving traffic through platforms like Instagram, TikTok, or LinkedIn.
- Paid Media: Investing in Google Ads, social ads, or other paid channels to supplement declining organic visibility.
- Strategic Partnerships and Affiliates: Collaborating with other businesses or influencers to reach new audiences.
The “traffic apocalypse” reported by some publishers[11] serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of single-channel reliance.
-
- Shift from Clicks to “AI Impressions” and Brand Citations: Organic visibility will increasingly be about being cited, summarized, or featured in AI-generated answers, even if it doesn’t result in a direct click. For many informational queries, an AI answer stating “According to [Your Brand],” or including your brand in a summarization, provides valuable brand awareness and authority. This means businesses need to optimize not just for direct traffic, but for “impressions” within the AI environment, recognizing that visibility in these snippets holds significant brand value.
- Content Strategy Evolution: The types of content that succeed will change. Generic, easily summarized “answer” content will become less valuable for driving direct traffic. Instead, businesses should focus on:
-
- Unique Value Proposition: Content that offers deeper insights, proprietary data, original research, or requires interactive elements that AI summaries cannot fully replicate. Examples include in-depth case studies, comparative tools, or exclusive interviews.
- Expert-Driven Content: Leveraging strong E-E-A-T signals to stand out. Content penned by recognized experts or industry leaders will carry more weight and be preferred by AI for its authority.
- Niche and Long-Tail Content: AI is adept at answering broad questions. Businesses can still capture traffic by targeting highly specific, long-tail queries and niche topics where human expertise and detailed information are still heavily sought after.
HubSpot’s data shows planned investments in how-to guides and in-depth reviews, precisely the kind of content that resists easy AI summarization[49].
-
- New Metrics for Success: SEO reporting will expand beyond traditional organic traffic, rankings, and conversions. Metrics like “AI citations,” “AI answer inclusion rate,” “share of voice in AI summaries,” and potentially engagement metrics for interactive AI SERP features will become important indicators of success. The value of being a source that AI confidently references will gain prominence.
- Industry-Specific Impacts: The implications will vary significantly by industry:
- Informational Sites (Blogs, Forums): Face cannibalization for simple questions but can thrive by offering deep dives, community features, or interactive tools (as seen with Stack Overflow’s adaptation to AI Q&A[11]).
- E-commerce: Less affected by AI for direct product search traffic, as product pages received <0.5% of AI referral clicks in one study[10]. However, they need to create robust informational content (buying guides, comparisons) to get noticed by AI and influence purchasing decisions indirectly.
- News Publishers: Facing an existential threat, leading some to pursue content licensing deals with AI companies (e.g., AP with OpenAI[12]) or even litigation (Penske Media Group against Google[13]) to ensure fair compensation and attribution. They will increasingly focus on direct audience engagement.
- Local Businesses: AI may provide direct answers for simple queries (e.g., store hours from Google Business Profile) but users will still click for directions, reservations, or specific information. Optimization for rich, accurate local data and voice search will be key.
- Ethical and Legal Considerations: The increased use of AI for content synthesis is raising concerns among content creators about intellectual property, fair use, and compensation. Lawsuits and content licensing deals are emerging, which could lead to new industry standards by 2026 regarding how AI models can access and monetize web content. Businesses need to stay abreast of these developments to protect their content and potentially explore new revenue streams through data licensing.
In essence, businesses reliant on organic search in 2026 must be proactive, adaptable, and focused on creating unique, high-quality content that either inspires direct engagement or provides authoritative source material for AI. The future of search visibility is less about “getting to #1” and more about “being the right answer, anywhere and everywhere.”
How Will AI Change Keyword Research and Content Creation Processes?
AI is fundamentally reshaping keyword research and content creation processes, offering unprecedented efficiencies while also demanding a higher standard of strategic thinking and human oversight. By 2026, these processes will be characterized by a symbiotic relationship between AI automation and human ingenuity.
Keyword Research Evolution:
Traditional keyword research, which often focuses on exact match terms and search volume, is evolving to encompass a deeper understanding of user intent and conversational patterns.
- Intent-Based and Semantic Analysis: AI tools can analyze search queries at scale, identifying underlying user intent (informational, navigational, transactional, commercial investigation) with greater accuracy. They can group semantically related keywords and topics, moving beyond keyword variations to thematic clusters. This allows SEOs to target broader topics rather than isolated keywords, ensuring comprehensive content coverage that satisfies varied user needs.
- Discovery of Conversational Queries: The rise of conversational AI encourages users to phrase queries as natural language questions. Google Ads data shows a nearly 2x increase in searches that are 7-8 words long since ChatGPT’s introduction[23]. AI-powered keyword research tools can now identify these longer, more specific, question-based queries, which are often overlooked by traditional methods. This helps content creators develop Q&A formats, comprehensive guides, and content structured to directly answer complex user questions.
- Predictive Analysis and Trend Spotting: Advanced AI models can analyze vast datasets to predict emerging trends and shifts in search behavior, allowing businesses to create content proactively for topics before they become saturated. This capability is invaluable for maintaining a competitive edge.
- Automated Competitor Analysis: AI can rapidly analyze competitor content, keyword portfolios, and backlink strategies, identifying gaps and opportunities that would take human researchers significantly longer to uncover.
While AI streamlines identification, the human element remains crucial for interpreting nuances, understanding context, and making strategic decisions based on AI-generated insights.
Content Creation Transformation:
AI is not just an assistant in content creation; it’s a powerful and pervasive force, influencing everything from ideation to initial drafting.
- Accelerated Drafting and Outlining: One of the most immediate impacts is AI’s ability to generate outlines, first drafts, and variations of content at speed. Marketers are leveraging AI to automate routine tasks, with 75% reporting reduced time spent on manual SEO tasks like drafting copy or analyzing data[7]. This frees up human writers to focus on higher-level tasks such as research, critical analysis, and adding unique perspectives.
- Content Ideation and Topic Expansion: AI can brainstorm content ideas, generate headlines, and suggest related topics based on keyword research and competitive analysis. This significantly expands the scope and creativity of content strategies.
- Localization and Personalization: AI can help adapt content for different audiences, languages, and regional nuances, improving relevance and engagement for diverse user bases.
- Quality Control and Human Curation Become Paramount: With AI flooding the web with content—over 50% of new online articles in late 2025 are AI-authored[9]—the distinction between valuable and generic content becomes critical. Google’s Helpful Content updates actively penalize “unhelpful” AI-generated text[8]. This makes the human review process indispensable. A staggering 93% of marketers continue to manually review and edit AI-generated content before publication, underscoring the necessity of human oversight for accuracy, tone, brand voice, and adding unique value[7].
- Focus on E-E-A-T and Authenticity: Content that truly stands out will be that which explicitly demonstrates human experience, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness. This translates to incorporating original research, firsthand accounts, unique case studies, and clearly attributing content to verified experts.
- Content Optimization for AI Consumption: Alongside human readability, content will need to be increasingly optimized for AI models. This includes clear, concise writing; logical structure; proper use of headings; and rich schema markup to make information easily extractable and summarizable by AI.
By 2026, content teams will likely adopt a “human-in-the-loop” model, using AI for efficiency and scale, but relying on human experts for strategic direction, quality assurance, creative input, and injecting the unique value that differentiates content in an AI-saturated environment. SEO professionals, 86% of whom already incorporate AI into their strategies[7], will act as orchestrators, blending AI capabilities with human expertise to achieve optimal visibility and engagement.
This deep dive into frequently asked questions illustrates the dynamic shift occurring in the SEO landscape. The next section will further explore emerging tools and technologies that are shaping this AI-driven future.
References
- Nearly 60% of Google searches end without a click in 2024
- Zero-click searches hit 60% in 2024: why traffic is a vanity metric | PAUL CLARKE posted on the topic | LinkedIn
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- Google attracts AI ire from publishers over content use, pushes licensing deals
- Google attracts AI ire from publishers over content use, pushes licensing deals
- Google disputes Pew study showing AI Overviews reduce clicks by half
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- Google disputes Pew study showing AI Overviews reduce clicks by half
- Google helpful content update
- ChatGPT reaches 100 million users two months after launch | Chatbots | The Guardian
- Stack Overflow is ChatGPT Casualty: Traffic Down 14% in March | Similarweb
- AI search is gaining traction, but it isn’t replacing Google: Survey
- AI search is gaining traction, but it isn’t replacing Google: Survey
- AI search is gaining traction, but it isn’t replacing Google: Survey
- Google vs Perplexity: AI chatbots drew just 2.96% of search traffic in 2024, new study finds | Technology News – The Indian Express
- Microsoft’s Bing Sees Modest Growth with ChatGPT Integration, But Google Still Leads the Search Market – Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) – Benzinga
- More users are trying Bing thanks to its GPT-4 integration, but they haven’t made a permanent switch
- More users are trying Bing thanks to its GPT-4 integration, but they haven’t made a permanent switch
- Half of new online articles written by AI, research shows
- 74% of New Webpages Include AI Content (Study of 900k Pages)
- 74% of New Webpages Include AI Content (Study of 900k Pages)
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- How search query length is shifting in the LLM era: Insights for brands
- How search query length is shifting in the LLM era: Insights for brands
- The Shift From SEO to AI Search: How Marketers Grow in 2026
- AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Top Platforms
- AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Top Platforms
- AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Top Platforms
- The Future of Google: Web Strategists Predict How AI Overviews & Other Search Changes Will Impact Traffic [New Data]
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- Nearly 60% of Google searches end without a click in 2024
- Zero-click searches hit 60% in 2024: why traffic is a vanity metric | PAUL CLARKE posted on the topic | LinkedIn
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- AI search is gaining traction, but it isn’t replacing Google: Survey
- AI search is gaining traction, but it isn’t replacing Google: Survey
- AI search is gaining traction, but it isn’t replacing Google: Survey
- Microsoft’s Bing Sees Modest Growth with ChatGPT Integration, But Google Still Leads the Search Market – Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) – Benzinga
- Microsoft’s Bing Sees Modest Growth with ChatGPT Integration, But Google Still Leads the Search Market – Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) – Benzinga
- More users are trying Bing thanks to its GPT-4 integration, but they haven’t made a permanent switch
- More users are trying Bing thanks to its GPT-4 integration, but they haven’t made a permanent switch
- ChatGPT reaches 100 million users two months after launch | Chatbots | The Guardian
- Stack Overflow is ChatGPT Casualty: Traffic Down 14% in March | Similarweb
- 74% of New Webpages Include AI Content (Study of 900k Pages)
- 74% of New Webpages Include AI Content (Study of 900k Pages)
- Half of new online articles written by AI, research shows
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 74% of New Webpages Include AI Content (Study of 900k Pages)
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- Google helpful content update
- Google helpful content update
- AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Top Platforms
- AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Top Platforms
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Top Platforms
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Top Platforms
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- 2023-07-13 | Exclusive: AP strikes news-sharing and tech deal with OpenAI
- 2024-05-23 | OpenAI to start using news content from News Corp. as part of a multiyear deal
- 2024-06-27 | Exclusive: Time strikes licensing deal with OpenAI
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- Nearly 60% of Google searches end without a click in 2024
- Zero-click searches hit 60% in 2024: why traffic is a vanity metric | PAUL CLARKE posted on the topic | LinkedIn
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- Google attracts AI ire from publishers over content use, pushes licensing deals
- Google disputes Pew study showing AI Overviews reduce clicks by half
- Google disputes Pew study showing AI Overviews reduce clicks by half
- Google disputes Pew study showing AI Overviews reduce clicks by half
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- AI search is gaining traction, but it isn’t replacing Google: Survey
- ChatGPT reaches 100 million users two months after launch | Chatbots | The Guardian
- 65% of Searches End Without Clicks
- Google vs Perplexity: AI chatbots drew just 2.96% of search traffic in 2024, new study finds | Technology News – The Indian Express
- More users are trying Bing thanks to its GPT-4 integration, but they haven’t made a permanent switch
- Microsoft’s Bing Sees Modest Growth with ChatGPT Integration, But Google Still Leads the Search Market – Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) – Benzinga
- Microsoft’s Bing Sees Modest Growth with ChatGPT Integration, But Google Still Leads the Search Market – Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) – Benzinga
- More users are trying Bing thanks to its GPT-4 integration, but they haven’t made a permanent switch
- How search query length is shifting in the LLM era: Insights for brands
- How search query length is shifting in the LLM era: Insights for brands
- Half of new online articles written by AI, research shows
- 74% of New Webpages Include AI Content (Study of 900k Pages)
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- Google helpful content update
- 60 AI SEO Statistics for 2025 | SeoProfy
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- The Future of Google: Web Strategists Predict How AI Overviews & Other Search Changes Will Impact Traffic [New Data]
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- Stack Overflow is ChatGPT Casualty: Traffic Down 14% in March | Similarweb
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- 2024-05-23 | OpenAI to start using news content from News Corp. as part of a multiyear deal
- 2023-07-13 | Exclusive: AP strikes news-sharing and tech deal with OpenAI
- More users are trying Bing thanks to its GPT-4 integration, but they haven’t made a permanent switch
- Microsoft’s Bing Sees Modest Growth with ChatGPT Integration, But Google Still Leads the Search Market – Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) – Benzinga
- Microsoft’s Bing Sees Modest Growth with ChatGPT Integration, But Google Still Leads the Search Market – Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) – Benzinga
- Stack Overflow is ChatGPT Casualty: Traffic Down 14% in March | Similarweb
- Google attracts AI ire from publishers over content use, pushes licensing deals
- Google attracts AI ire from publishers over content use, pushes licensing deals
- 2023-07-13 | Exclusive: AP strikes news-sharing and tech deal with OpenAI
- 2024-05-23 | OpenAI to start using news content from News Corp. as part of a multiyear deal
- 2024-06-27 | Exclusive: Time strikes licensing deal with OpenAI
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- Do people click on links in Google AI summaries? | Pew Research Center
- 2024 Zero-Click Search Study: For every 1,000 EU Google Searches, only 374 clicks go to the Open Web. In the US, it’s 360. – SparkToro
- 2024 Zero-Click Search Study: For every 1,000 EU Google Searches, only 374 clicks go to the Open Web. In the US, it’s 360. – SparkToro
- Nearly 60% of Google searches end without a click in 2024
- Nearly 60% of Google searches end without a click in 2024
- AI search is gaining traction, but it isn’t replacing Google: Survey
- AI search is gaining traction, but it isn’t replacing Google: Survey
- ChatGPT reaches 100 million users two months after launch | Chatbots | The Guardian
- Google vs Perplexity: AI chatbots drew just 2.96% of search traffic in 2024, new study finds | Technology News – The Indian Express
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- Study: ChatGPT & AI Tools Gain Ground In Search Market
- 74% of New Webpages Include AI Content (Study of 900k Pages)
- 74% of New Webpages Include AI Content (Study of 900k Pages)
- Half of new online articles written by AI, research shows
- AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Top Platforms
- AI Traffic in 2025: Comparing ChatGPT, Perplexity & Other Top Platforms
- Stack Overflow is ChatGPT Casualty: Traffic Down 14% in March | Similarweb
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- Publishers race against Google Zero doomsday clock
- Google attracts AI ire from publishers over content use, pushes licensing deals
- Google attracts AI ire from publishers over content use, pushes licensing deals
- Microsoft’s Bing Sees Modest Growth with ChatGPT Integration, But Google Still Leads the Search Market – Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) – Benzinga
- Microsoft’s Bing Sees Modest Growth with ChatGPT Integration, But Google Still Leads the Search Market – Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT) – Benzinga
- The Future of Google: Web Strategists Predict How AI Overviews & Other Search Changes Will Impact Traffic [New Data]
- The Future of Google: Web Strategists Predict How AI Overviews & Other Search Changes Will Impact Traffic [New Data]